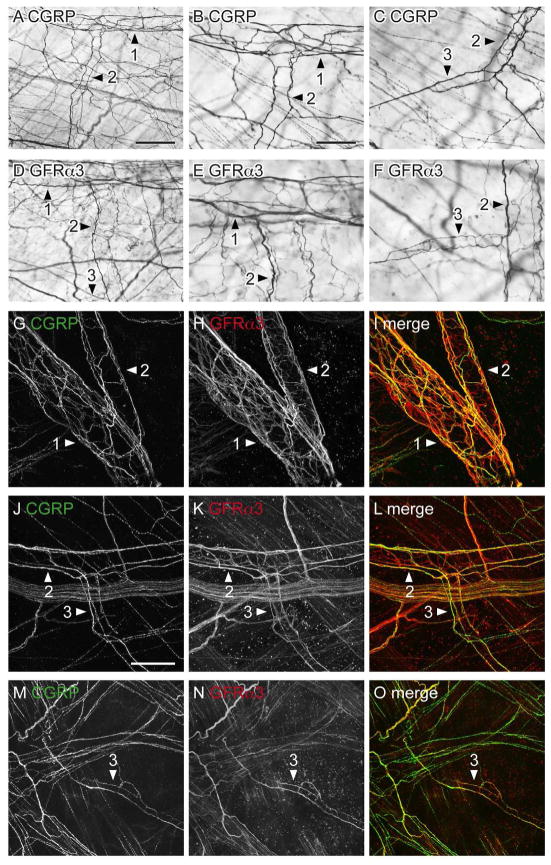
Figure 5.
CGRP- and GFRα3-immunoreactive (IR) axons associated with the bladder vasculature as viewed in whole mounts. Panels A–F show diaminobenzidine (DAB)-processed tissue viewed with conventional microscopy whereas G–O are confocal micrographs of immunofluorescence. Numbered arrowheads indicate primary, secondary and tertiary branches of the vascular tree. A–C: Many CGRP-IR para-vascular axons were found on the primary, secondary (A, B) and tertiary (C) branches of the vascular tree; peri-vascular axons were also found on the primary branch but were sparse on subsequent branches. D–F: Para- and peri-vascular GFRα3-IR axons were associated with all branches of the vascular tree. G–I: Many para-vascular CGRP- and GFRα3-IR axons were associated with the primary and secondary branches of the vascular tree; GFRα3-IR peri-vascular axons were more prevalent than CGRP-IR peri-vascular axons on these branches. J–I: CGRP- and GFRα3-IR para-vascular axons were associated with secondary and tertiary vessel branches; many GFRα3-IR peri-vascular axons were present in these branches. m–o: Neither CGRP- nor GFRα3-IR para-vascular axons extended to the most distal aspects of the vascular tree. Images (G–O) are confocal z-stacks (thickness: G–I, 45 μm; J–L, 28 μm; M–O, 30 μm; all with 1 μm step size). Scale bar = 200 μm in (A) also applies to (D); 100 μm in (B) also applies to (C, E, F); 100 μm in (g) also applies to (H, I); 100 μm (J) also applies (K, L); 100 μm in (M) also applies to (N, O). CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; GFRα3, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family receptor α3.