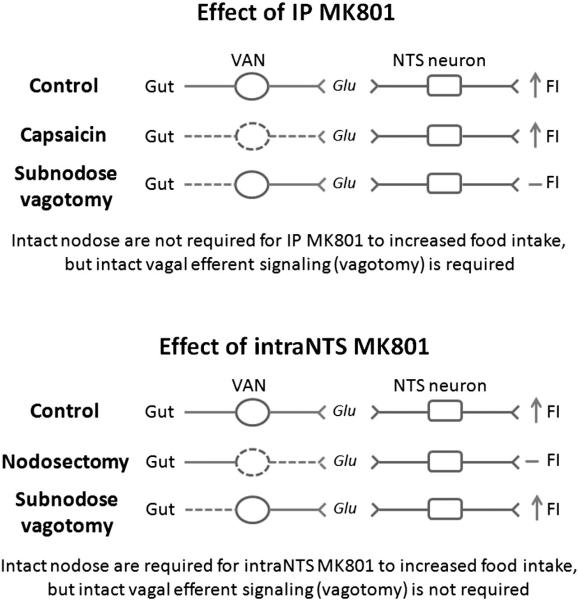
Fig. 2.
Systemic MK801 and intraNTS MK801 activate different pathways. Both intraperito-neal and intraNTS administration of MK801 increase food intake. An intact vagus nerve is required for systemic MK801 as demonstrated by the fact that vagotomy inhibits the increases in food intake caused by IP MK801. However, vagal afferent neurons, as demonstrated by capsaicin treatment, are not required for the orexigenic effects of systemic MK801. Therefore vagal efferent neurons modulate the feeding effects of IP MK801. Conversely, intraNTS MK801 was inhibited by nodosectomy, but not by sub-nodose vagotomy. This suggests that vagal afferent neurons modulate the feeding effects of intraNTS MK801. Thus, systemic MK801 and intraNTS MK801 administration activate different pathways.