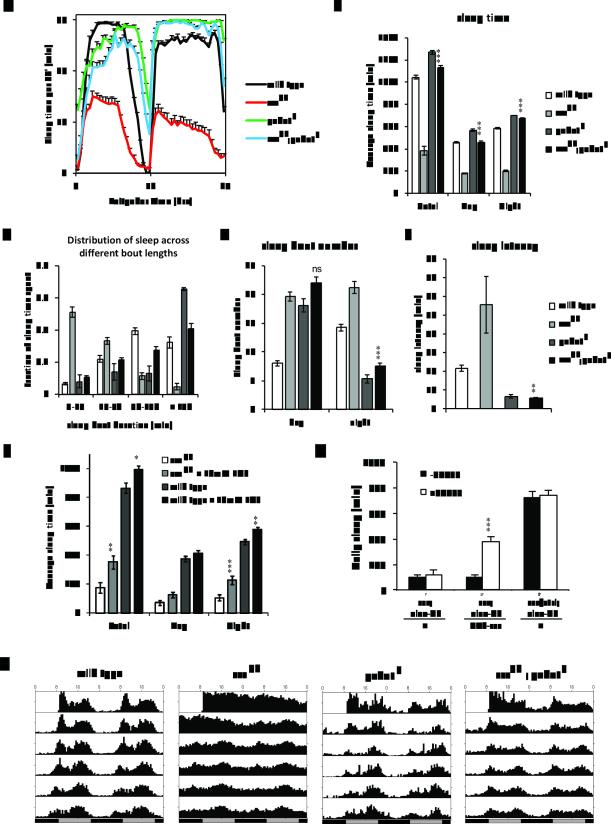
Figure 3.
Disruption of gabat completely suppresses the short sleep phenotype of sssp1 flies. To determine the effect of the gabat mutation on the sss phenotype, sssp1;gabatf male flies were compared with sssp1, gabatf and wild type control flies for daily sleep profiles (A), sleep time (B), distribution of sleep with respect to the length of sleep episodes (C), number of sleep bouts (D), and sleep latency (E). (F) Inhibition of GABAT in adults partially rescues the sss mutant. We treated wild type and sss flies with an inhibitor specific for GABAT, EOS, and compared day, night, and total sleeptime. sssp1 and wild-type males (between 1-5 days of age) were fed either 10mM EOS or control food for 5 days. We averaged sleeptime of flies from days 3-5 to ensure that the drug was ingested. (G) The sssP1 phenotype results from adult and developmental effects. To restrict sss expression to adults, we used an elav-GS driver to conditionally rescue sssp1 adults. Daily sleep was monitored in females in the presence (white bar) or absence (black bar) of 500μM RU486. Heterozygous (sss/ctrl) flies were included as positive controls. (H) gabatf improves circadian rest:activity rhythms of sssp1. Male flies were first entrained to 12:12 Light:Dark cycles at 25°C for 4 days before the flies were transferred into constant darkness for assay of free-running rhythms. The figure shows average 30 minute activity bins from flies of the respective groups recorded for 7 days in continuous darkness (DD), starting from day 1 (DD1). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test was used to examine the differences in sleep time, bout number, and latency. Asterisks depict the results of statistical tests between sssp1 and sssp1;gabatf (B-E) or control and EOS-treated sssp1 and wild-type flies (F) ***, P<0.001; **, P<0.01; ns, not significant. MWU test was used to test for differences in sleep bout distribution. gabatf rescued the short sleep bout duration phenotype of sss (MWU test with Bonferroni adjustment, sssp1 vs sssp1;gabatf P<0.0001; gabatf vs sssp1;gabatf, P=0.92). Unpaired t-tests with Bonferroni correction were used to test for differences in daily sleep in (G). *** P<0.001.