Figure 3.
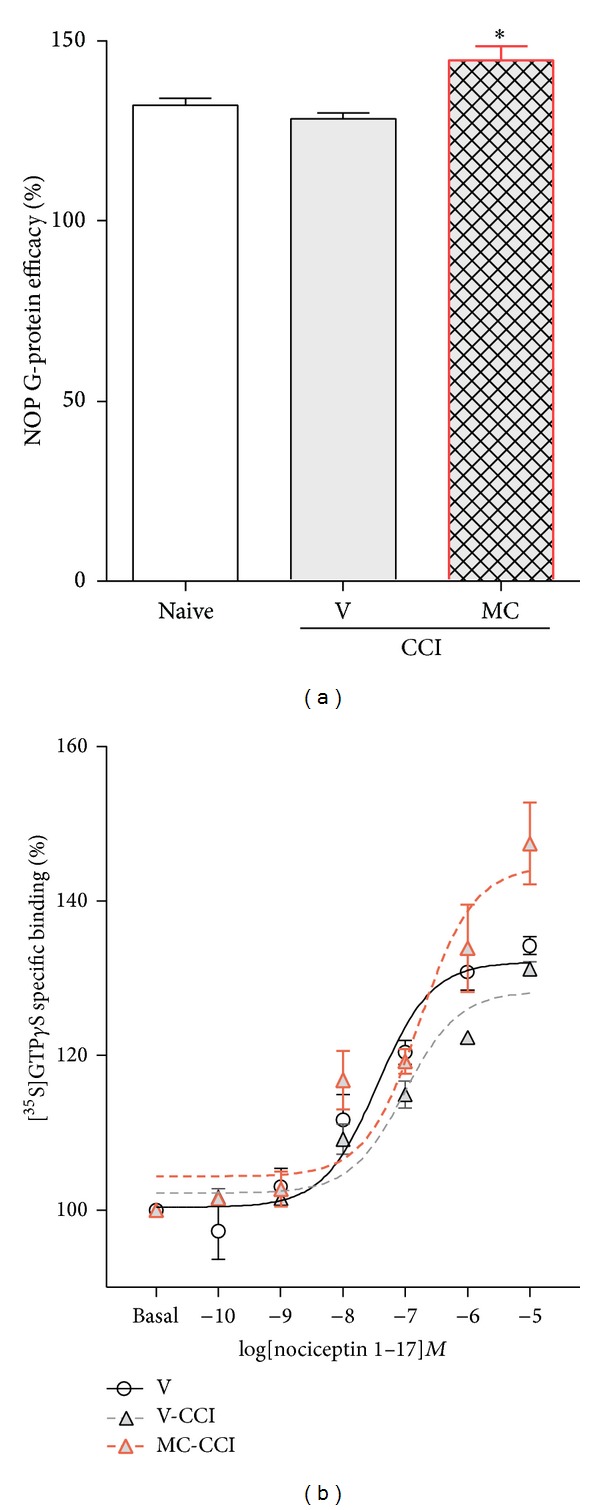
Repeated minocycline administration influenced NOP signaling. Chronic i.p. (30 mg/kg) minocycline treatment significantly increased the specific binding of the nucleotide analogue on NOP G-protein compared to vehicle-treated CCI-exposed rats. (a) The figure represents the calculated efficacy (or E max) of the NOP-mediated G-protein during ligand stimulation. (b) The figure represents the specifically bound [35S]GTPγS as a percentage in the presence of increasing concentrations (10−10−10−5 M) of N/OFQ 1–17. Basal activity was settled as 100%. Points and columns represent mean ± SEM. for at least three experiments performed in triplicates. Intergroup differences were analyzed using ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05 indicates significant differences compared with naïve rats. V: vehicle, MC: minocycline.
