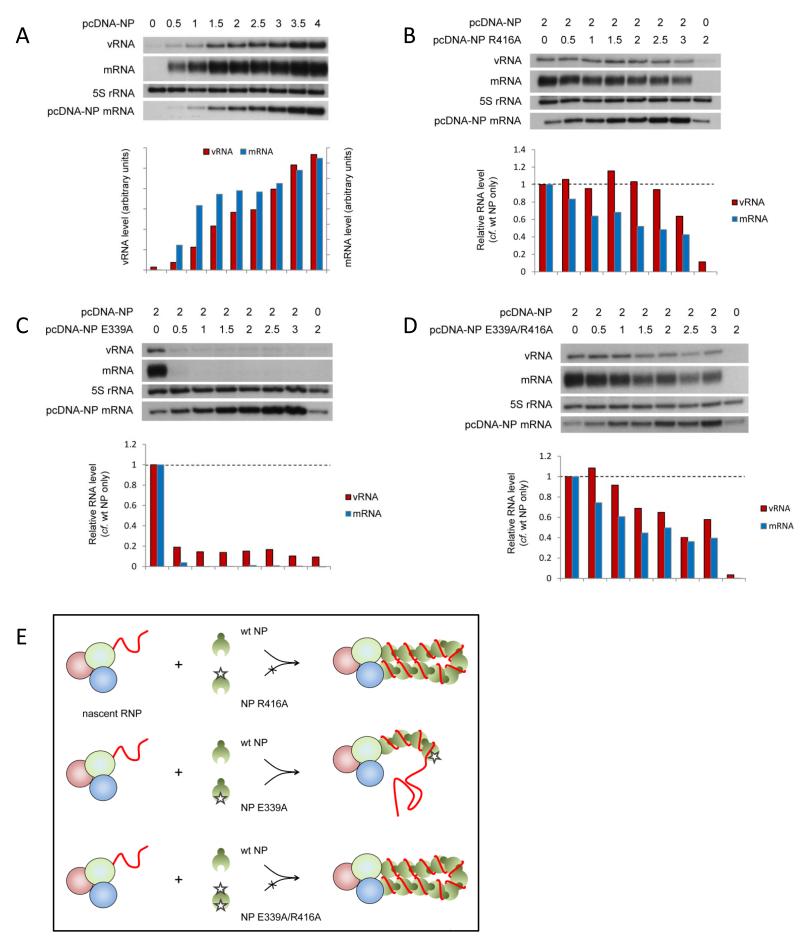
Fig. 6. Directionality of NP assembly onto RNP complexes.
(A-D) The accumulation of vRNA and mRNA following in vivo reconstitution of vRNPs from trimeric polymerase and full length segment 5 vRNA in the presence of varying concentrations of wild type NP (A) or wild type and oligomerisation mutant [R416A (B), E339A (C) or E339A/R416A (D)] NP was analysed by primer extension. 0.5μg of each of the polymerase subunit-expressing plasmids and the plasmid expressing the full length segment 5 RNA template (containing mutations to prevent expression of NP) were transfected together with the amount of NP-expressing plasmid shown in μg [in a total of 6μg (A) or 7μg (B-D)]. Analysis of the 5S rRNA levels served as an internal control. The level of mRNA derived from the NP-expressing plasmid is also shown. Quantification was performed by phosphorimage analysis. Graphs depicting the vRNA and mRNA levels accumulating in the presence of varying concentrations of wild type and mutant NP relative to those accumulating in the presence of wild type NP alone are shown. (E) Schematic depiction of competition assays demonstrating the directional assembly of NP onto nascent RNPs by homo-oligomerisation. NP recruitment to the nascent RNP is mediated through NP homo-oligomerisation, the tail loop of the incoming NP interacting with the insertion groove of the resident NP.