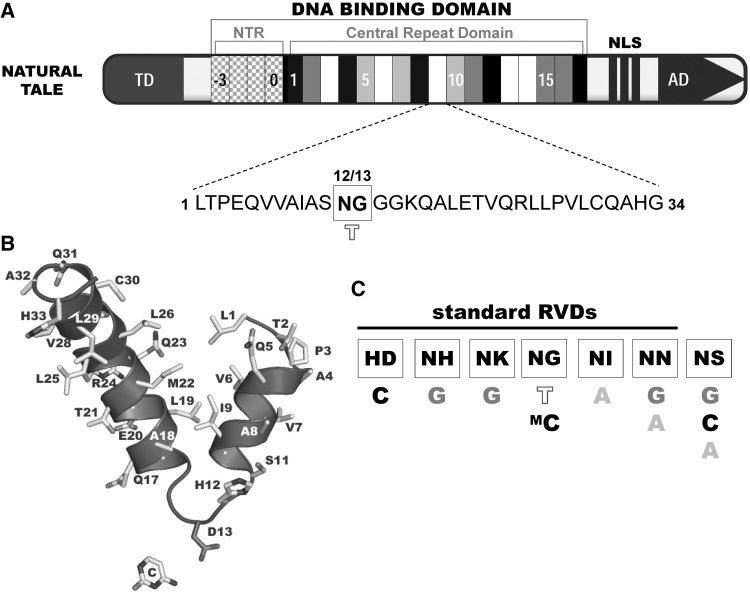
Figure 1:
TALE domain composition and DNA-binding code. (A) TALEs contain nuclear localization signals (NLS) and an activation domain (AD) to function as transcriptional activators. A central tandem repeat domain confers specific DNA-binding and host specificity. Translocation signal (TD) and four cryptic repeats required for initiation of DNA binding and for the recognition of 5′-T0 are located at the N-terminus (chequered rectangles). Each 34 amino acid (aa) long repeat in the CRD binds to one nucleotide with specificity determined mainly by aa at position 13. One sample repeat is shown below the protein scheme. Numbers 12/13 refer to aa positions within the repeat. (B) Structure of an individual TALE repeat module. The repeat has 34 amino acids in length and takes a loop–helix secondary structure where two α-helices are linked by short ‘RVD loop’. The residue 13 is responsible for preferential binding of the repeat module to a single specific nucleotide in the major groove of target DNA sequence (C, in this case). (C) Repeat types have specificity for one or several nucleotides. Only bases of the DNA leading strand are shown. Adapted from [7, 9, 10, 11].