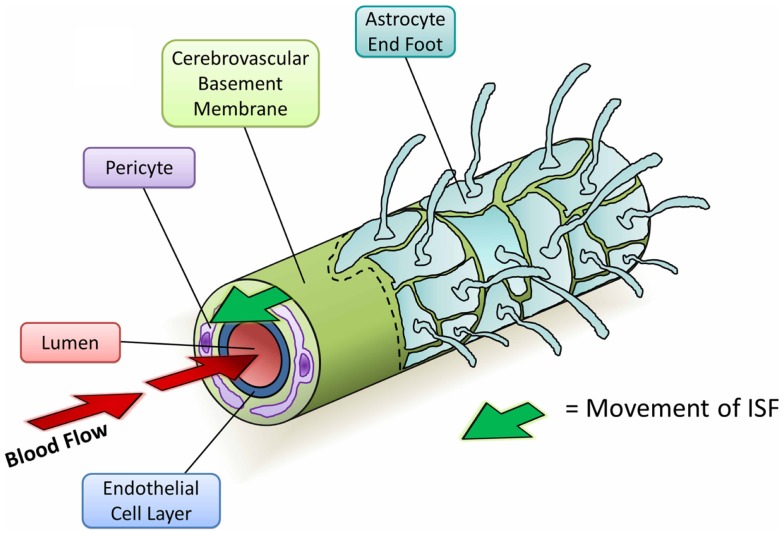
Figure 4.
Diagram depicting the perivascular elimination of solutes along the cerebrovascular basement membrane of a cerebral capillary. The arterial pulsatile wave driving blood flow into the brain (red arrows) is followed by a refractory wave, which may drive the movement of interstitial fluid (ISF) out of the brain along the cerebrovascular basement membrane (green arrow). Conformational changes in cerebrovascular basement membranes during the refractory wave may provide a valve-like mechanism that promotes unidirectional flow of ISF. Viewed from the center: capillary lumen (red), endothelial cell layer (blue), cerebrovascular basement membrane (light green), pericyte (purple), and astrocyte end foot (teal) with a section removed beyond dotted line.