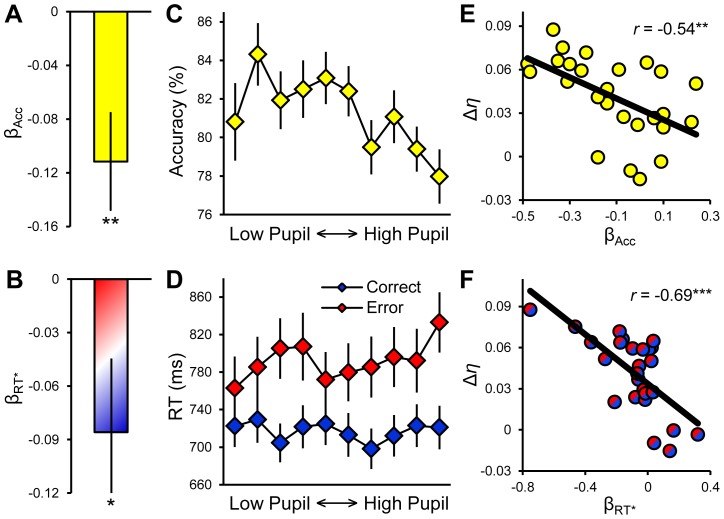
Figure 3. Pupil diameter correlates with response accuracy and the discrepancy between correct and error RTs.
A. Mean of β coefficients from within-subjects logistic regressions of trial-by-trial response accuracy on baseline pupil diameter (Equation 1, Materials & Methods ). B. Mean βs for the interaction term of within-subjects linear regression models designed to explore the relationship between baseline pupil diameter and RT (Equation 2, Materials & Methods ). The effect illustrates the increased discrepancy between correct and error RTs as a function of increasing pupil diameter. C,D. Response accuracy (C) and RT (D) sorted within-subjects by baseline pupil diameter into 10 equal-sized bins, illustrating the predominantly linear nature of the relationships. E. The strength of the subject-specific relationship between pupil diameter and response accuracy (β Acc) was correlated with the change in drift rate variability from low to high pupil bins (Δη). F. The strength of the relationship between pupil diameter and the discrepancy between correct and error RTs (β RT*) was also correlated with Δη. Error bars = S.E.M. *** = p<0.001, ** = p<0.01, * = p<0.05.