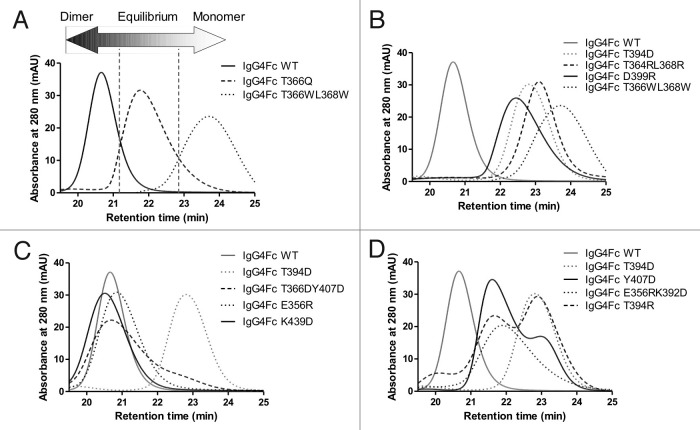
Figure 2. Representative HPLC chromatograms showing how mutations can influence the monomer-dimer equilibrium. (A) IgG4 Fc wild type (solid line), IgG4 Fc T366Q (dashed line) and IgG4 Fc T366WL368W (dotted line) are dimeric, in monomer-dimer equilibrium and monomeric respectively. (B) Variants showing predominantly monomeric behavior, IgG4 D399R (solid line), IgG4 T364RL368R (dashed line), and IgG4 T349D (dotted line). (C) Variants showing equilibrium or mixed behavior, IgG4 Y407D (solid line), IgG4 T394R (dashed line), and IgG4 E356RK392D (dotted line). (D) Variants showing dimeric behavior, IgG4 K439D (solid line), IgG4 T366DY407D (dashed line), and IgG4 E356R (dotted line). In each of (B), (C), and (D) chromatograms are shown relative to IgG4 Fc wild type (solid line), and IgG4 Fc T366WL368W (dotted line) in a gray trace.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.