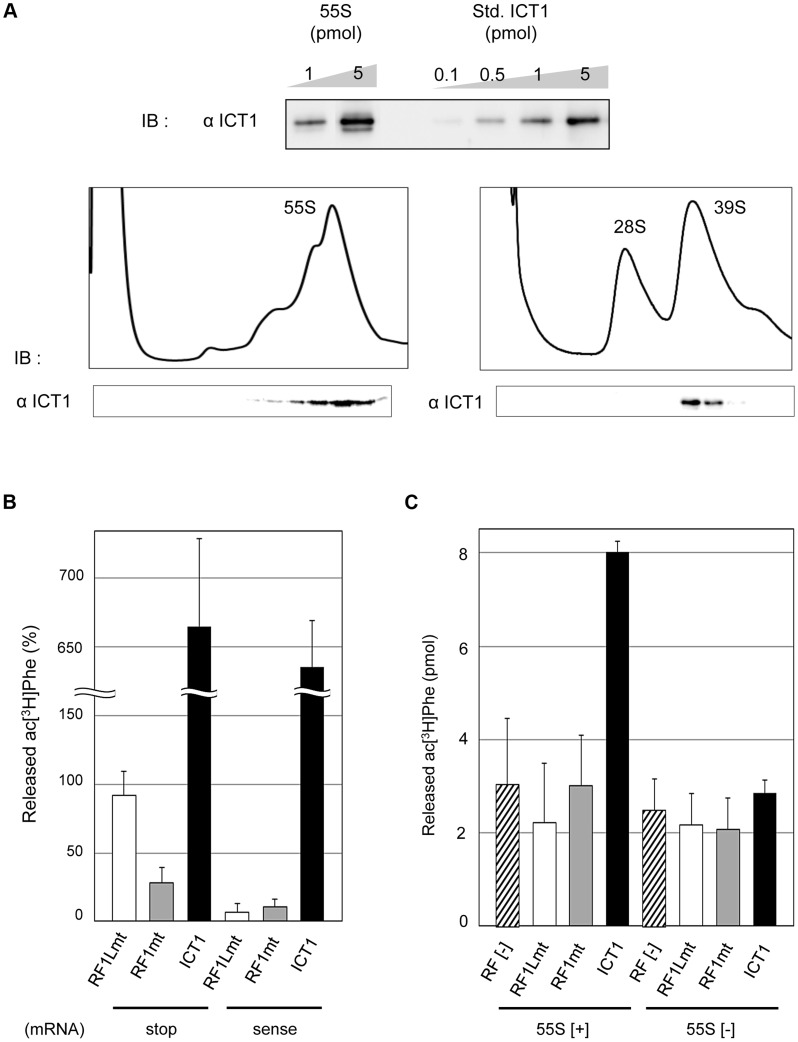
Figure 1. ICT1 shows codon-independent peptide-release activity on 55S mitoribosomes.
(A) ICT1 is integrated within the 39S large mitoribosomal subunit in a 1∶1 stoichiometry. The amounts of 55S-integrated ICT1 on 55S ribosomes were estimated by Western blotting, using the purified ICT1 protein as a standard (Std. ICT1; upper panel). 55S mitoribosomes (lower left panel) or mitoribosomal subunits (lower right panel) were separated on 15%–30% (w/v) sucrose gradients (containing 10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 80 mM NH4Cl, 8.2 mM MgSO4, and 1 mM DTT, for 55S; 10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 200 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM GDP and 1 mM DTT, for subunits), and the fractions were analyzed by Western blotting with an ICT1 antibody. IB, immunoblotting. (B) Exogenous ICT1 exhibits codon-independent peptide-release activity on 55S mitoribosomes. The ac[3H]Phe release activities of ICT1, RF1Lmt and RF1mt on 55S ribosomes were tested in the presence of mRNAs and ac[3H]Phe-tRNAPhe. Ribosomes were programed by mRNAs encoding MF-UAA (stop) or MFV (sense). The results were evaluated relative to the 100% value, when all of the ac[3H]Phe-tRNAPhe bound to ribosome was hydrolyzed; 100% value corresponds to 0.9 pmol of ac[3H]Phe. Results represent the average of at least three independent experiments. The error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). (C) ICT1 shows peptide release activity on 55S mitoribosomes in the absence of mRNA. Peptide-release assays on 55S ribosomes were performed as in (B), but in the absence of mRNA. 55S [+] and 55S [−] indicates the assays in the presence and absence of 55S mitoribosomes, respectively. Results represent the average of at least three independent experiments. The bars on the graph indicate SD.