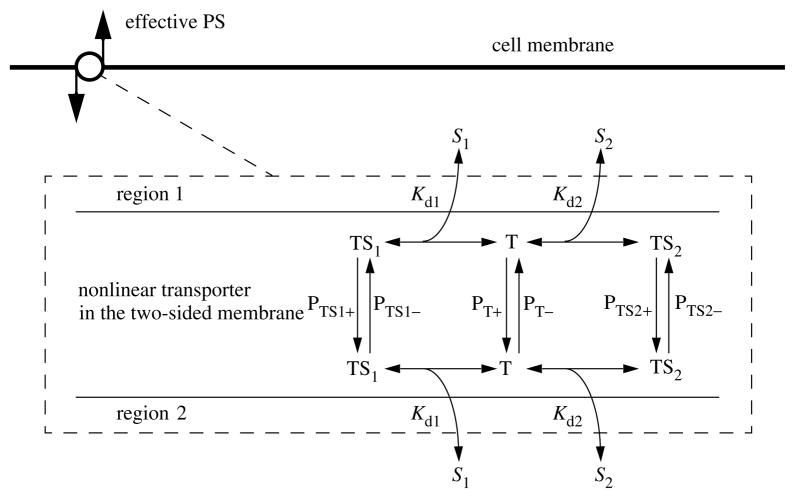
Figure 3.
Competitive transporter kinetics. Solutes S1 and S2 compete for the binding site on the transporter and may have differing affinities and translocation rates. At high substrate concentrations on both sides, this transporter becomes an obligatory counter-transporter, forcing one-to-one exchange. The P’s are unidirectional permeabilities (cm s−1), and in the model are multiplied by membrane surface area, the Kd’s are dissociation constants (Molar) and the TS’s and T’s are the concentrations of transporter in the three forms on either one side of the membrane or the other, with units of concentration in moles per unit surface area on each side.