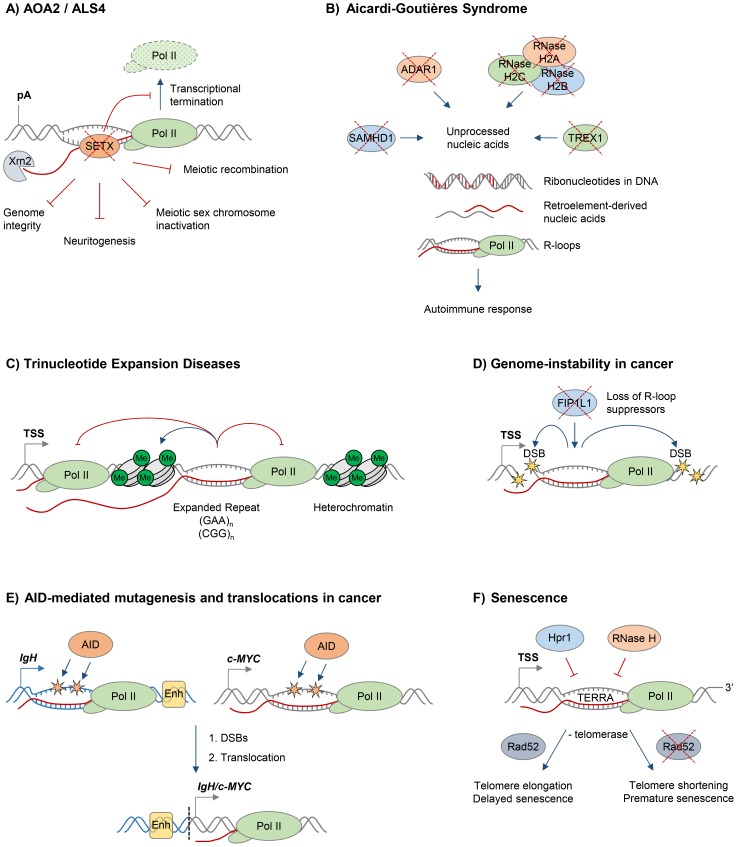
Figure 2. R-loops and human diseases.
The diagram depicts the role of R-loops in human diseases. Loss of wild type protein function is depicted by red crosses. A. Ataxia and motor neuron diseases. Mutations in human RNA/DNA helicase senataxin are associated with AOA2/ALS4 disorders and lead to R-loop accumulation and defects in transcriptional termination by Pol II [16], the maintenance of genome integrity [46], meiotic recombination during spermatogenesis, gene silencing during meiotic sex chromosome inactivation [14], and neuronal differentiation [49]. B. Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS). AGS is associated with mutations in all three subunits of RNase H2, ssDNA 3′–5′ exonuclease TREX1 (DNASEIII), dsRNA-editing enzyme ADAR1, and dNTP triphosphatase SAMHD1; these trigger accumulation of unprocessed nucleic acids, including genomic DNA with incorporated ribonucleotides, R-loops, and retroelement-derived nucleic acids, and result in the immune response characteristic of AGS [65]. C. Trinucleotide expansion diseases. R-loops form over expanded repeats and result in decreased initiation and elongation of RNA Pol II and formation of repressive chromatin marks, which silence the host gene containing expanded repeats [75]. D. Genome instability in cancer. Loss of proteins protecting against abnormal R-loop accumulation, such as FIP1L1, leads to genome instability, one hallmark of cancer [31]. Yellow stars denote double-stranded DNA breaks. E. AID-mediated mutagenesis and translocations in cancer. Single-stranded DNA in R-loops is a substrate for cytidine deamination by activation-induced cytidine deaminase, leading to mutagenesis as indicated by orange stars [21], [88]. These mutations can cause DSB formation, leading to chromosomal translocations. The IgH/c-MYC translocation brings the strong IgH enhancers, shown as yellow box, close to c-MYC, leading to its overexpression in Burkitt's lymphoma [87]. Transcription of IgH/c-MYC starts from a previously inactive promoter downstream of the translocation break point. The IgH locus is depicted in blue, c-MYC gene is in grey. The translocation breakpoint is indicated by a dashed black line. F. Senescence. R-loops formed by the noncoding RNA TERRA accumulate at telomeres in cells deficient of Hpr1 and RNase H. In the absence of telomerase, these R-loops promote Rad52-dependent telomere elongation and delayed senescence. In the absence of telomerase and Rad52, R-loops promote telomere shortening and premature senescence [94].