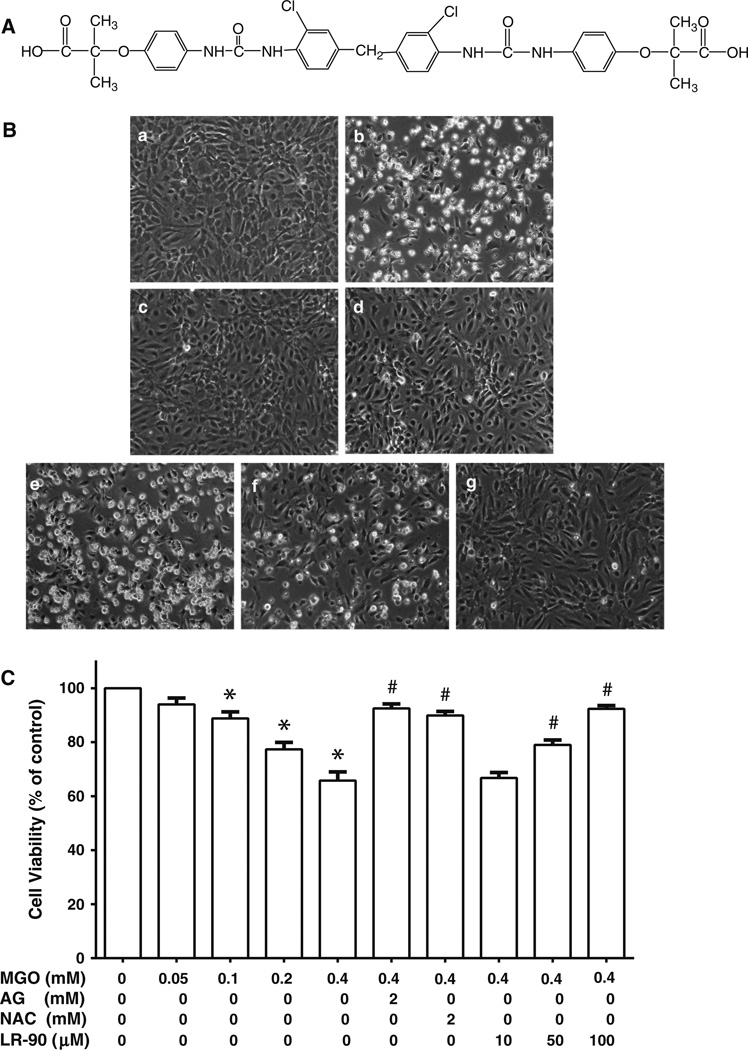
Fig. 1.
Effects of LR-90 on MGO-induced cell death in HUVECs a Chemical structure of LR-90, methylene bis 4,4′-(2-chloropheny-lureidophenoxyisobutyric acid). b Representative phase contrast photomicrographs of MGO-treated cells with and without test compounds. HUVECs were treated for 24 h with a 0.1 % DMSO (vehicle control); b MGO (0.4 mM); c MGO + 2 mM AG; d MGO + 2 mM NAC; e–g MGO + 10, 50, or 100 µM LR-90, respectively. Original magnification: 160x. c Percentage of viable cells analyzed by MTT assay after 24 h exposure to MGO in the presence of various concentrations of test compounds. Data on graph were from three independent experiments (n = 9) and were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test (*p < 0.05 vs. vehicle control and # p < 0.05 vs. 0.4 mM MGO treatment only)