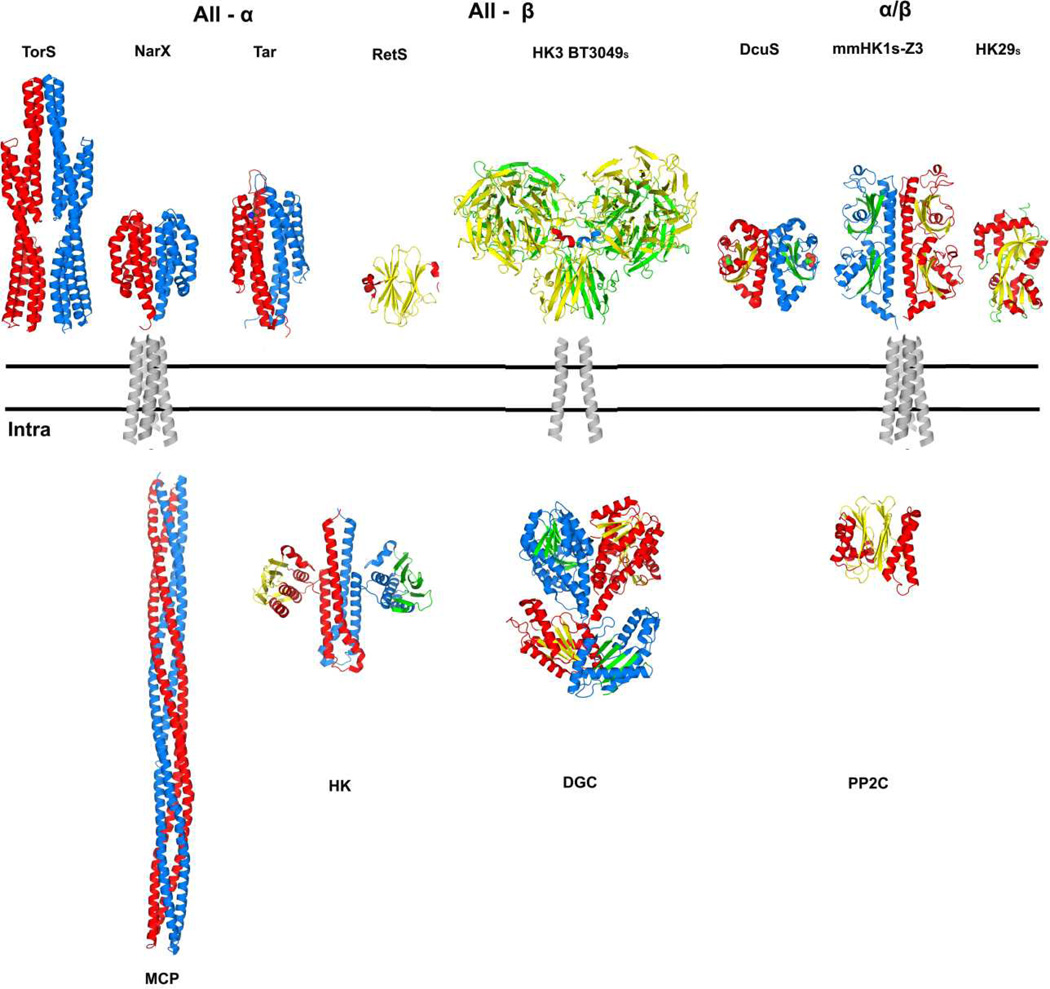
Figure 7. Summary of diverse, variably associated transmembrane receptor systems.
The double lines represent the plasma membrane. Alternative extracellular / periplasmic sensor domains are shown above the membrane and alternative cytoplasmic signaling portions are shown below the membrane. A transmembrane domain connects the outside to the inside in diverse combinations. Structure figures were generated PyMol [69] from PDB files as indicated: TorSS (3O1H; [22]), NarXS (3EZH; [15]), TarS (2LIG; [74]), RetSS (3JYB; [45]), HK3 BT3049S (3V9F; this work), DcuSS (3BY8; [75]), HK1S-Z3 (3LIB; [29]), HK29s (3H7M; [76]), transmembrane domains (1H2S; [39]), MCP (2CH7; [77]), HK (2C2A; [23]), DGC (2WB4; [78]) and PP2C (2XZV; [79]). All structures are shown as dimers except for RetSS, PP2C and HK29S. The coloring for one protomer has helix (red) and sheet (yellow); that for the partner protomer has helix (blue) and sheet (green). The four-helix bundle transmembrane domain is shown as representative for conventional all-helix (e.g. NarX or Tar) and PDC-domain (e.g. DcuS or HK1) receptors; a two-helix transmembrane domain is shown for the unconventional HK3 receptors, which connect to various signaling components in the cytoplasm.