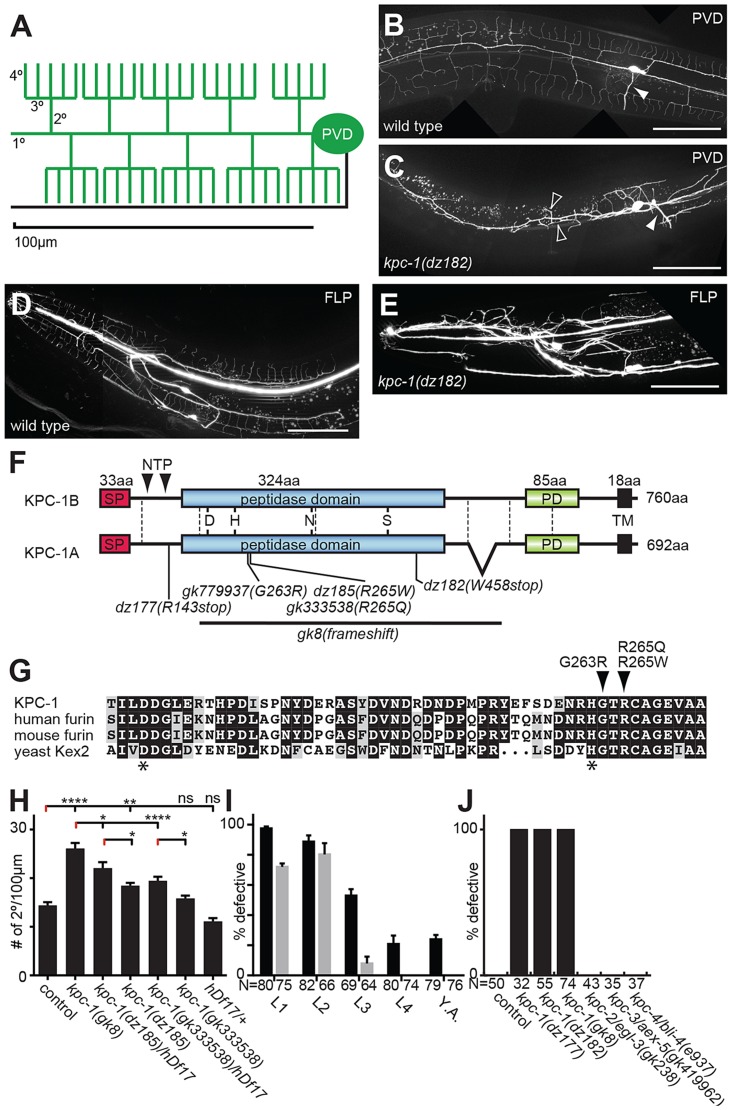
Figure 1. KPC-1 is required for development of dendritic arbors.
A Schematic of the PVD somatosensory neuron with dendrites (including primary/1°, secondary/2°, tertiary/3° and quaternary/4° branches) and the axon indicated in green and black, respectively. B–C Lateral view of an adult wild type (B) and kpc-1(dz182) mutant animal (C). PVD sensory neurons are visualized by a fluorescent reporter (wdIs52). Anterior is to the left and scale bars indicate 50 µm in all panels. An arrowhead denotes the PVD axon. Open arrow heads indicate ectopic 3° branches. D–E Images of an adult wild type animal (D) and a kpc-1(dz182) mutant animal (E). FLP sensory neurons are visualized by a fluorescent reporter (muIs32). F Schematic of KPC-1 with domains (SP: signal peptide, PD: P domain, TM: transmembrane domain) and exon boundaries (dashed lines) indicated. KPC-1 exists in a long and a short splice variant. All experiments were conducted with the short KPC-1A variant. Mutant alleles and predicted molecular changes are shown. NTP (N terminal propeptide) indicates cleavage sites that are necessary for autoproteolytic activation of the proprotein. G Partial sequence alignment of the peptidase domain in KPC-1 (NP_001021101), human furin (NP_002560.1), mouse furin (NP_001074923.1), and yeast Kex2 (NP_014161) protein. Asterisks indicate the aspartic acid and histidine of the catalytic triad. Alignments were obtained using Multalin (http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr) and rendered with Boxshade (http://www.ch.embnet.org). For a Full alignment see Figure S1. H Quantification of the number of secondary branches in the genotypes indicated. hDf17 is a chromosome I deficiency allele that deletes the entire kpc-1 locus. Data are represented as mean +/− SEM. Statistical comparisons were performed using one-sided ANOVA with the Tukey correction. Statistical significance is indicated (*, P≤0.05; **, P≤0.01; ****, P≤0.0001, ns: not significant (P>0.05)). N = 22 animals (302 dendritic branches) of wild type control; N = 22 animals (548 dendritic branches) of kpc-1(gk8); N = 16 animals (331 dendritic branches) of kpc-1(dz185)/hDf17; N = 26 animals (461 dendritic branches) of kpc-1(dz185), N = 16 animals (292 dendritic branches) of kpc-1(gk333538)/hDf17, N = 26 animals (396 dendritic branches) of kpc-1(gk333538). I Quantification of animals with defects in PVD at the young adult stage following RNAi mediated knock down of kpc-1 (grey bars) or GFP as a control for RNAi efficacy (black bars) using the hypersensitive eri-1(mg366); wdIs52 reporter background at 15C°. All animals were assayed as 2 day old adults and the developmental stage at which knock down was initiated is shown. Animals were arbitrarily defined as defective, if they displayed excessive ectopic branching proximal to the cell body, coupled with complete lack of quaternary branches anterior to the vulva or, GFP was absent in PVD. Note, that while knock down of GFP initiated at late developmental stages is still effective, no effects are seen at these stages as a result of kpc-1 knock down. J Quantification of animals with defects in PVD in the genotypes indicated (See also Figure S6). Defective animals were defined as in I.