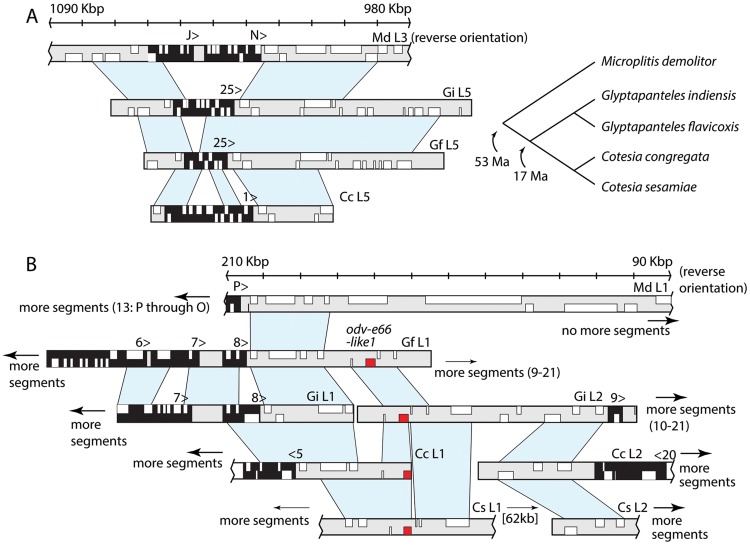
Figure 4. Two genomic regions flanking proviral segments are conserved among BV-carrying wasps.
(A) The area surrounding segments N and J in M. demolitor Locus 3 is homologous to the regions surrounding segment 25 in Locus 5 of G. flavicoxis and G. indiensis and segment 1 in Locus 5 of C. congregata. M. demolitor loci are oriented to match the orientation of sequence scaffolds and similarity between flanking regions reported in prior studies. Although the genes in the proviral segments themselves are usually not recognizably homologous (black background with genes in white), the regions flanking these proviral segments (gray background with genes in white) are conserved as indicated by regions of synteny shaded in light blue. To the right of the figure is shown the phylogenetic relationships between these wasp species and estimated divergence times. (B) The downstream region flanking segment P in M. demolitor Locus 1 is similar to the region between Locus 1 and 2 in G. flavicoxis, G. indiensis, C. congregata and C. sesamiae Kitale. Genes and segments are depicted as in (A) except for odv-e66-like1 homologs are indicated in red in the Glyptapanteles and Cotesia genomes. Although the odv-e66 homologs are located in an area of synteny, no odv-e66 homologs exist in this region for M. demolitor. Accession numbers for sequences are MdL3 (KK043340), GiL5 (EF710656), GfL5 (EF710650), CcL5 (HF586476), MdL1 (KK044729), GfL1 (EF710644), GiL1 (EF710657), GiL2 (AC191960), CcL2 (HF586473), CcL1 (HF586472), CsL2 (EF710635), CsL1 (EF710629).