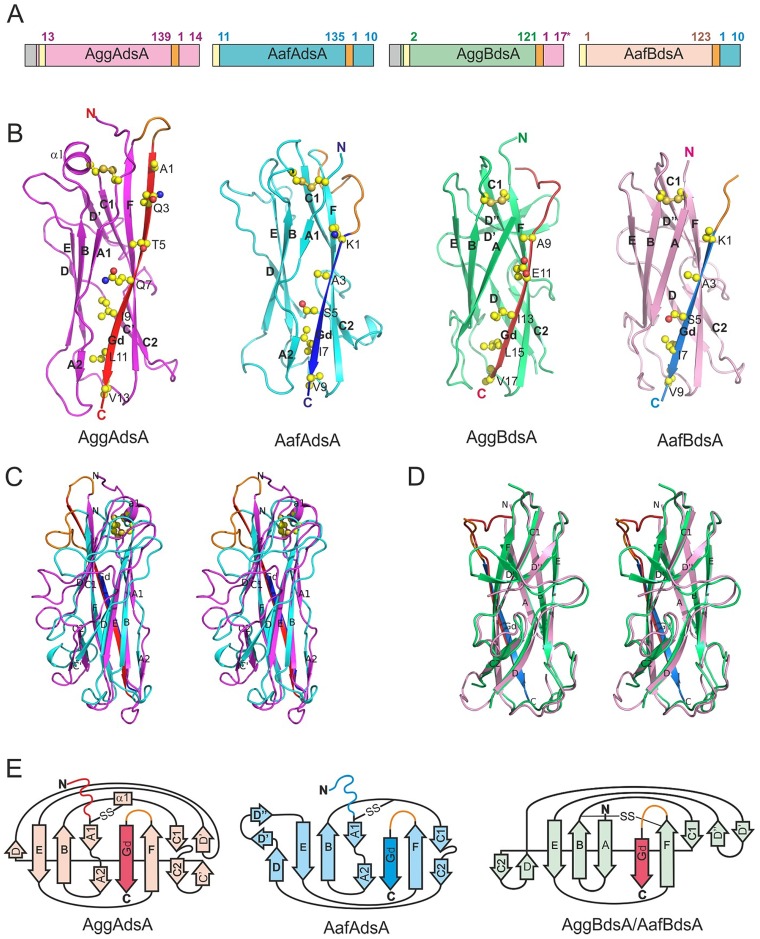
Figure 2. High-resolution structures of DSC subunits of AAF type I and II.
(A) Schematic representation of DSC monomers. The positions of residues flanking mature sequence are numbered. Signal peptide, N-terminal His-tag, and linker are colored in grey, yellow and orange, respectively. For AggBdsA, both donor strand sequences of AggA from the German outbreak strain and classical EAEC strain 17–2 (three residue longer) were used successfully to stabilize AggB, however only the later crystallized. Amino acid sequences of the constructs are shown in Fig. S2. (B) Cartoon diagrams of AggAdsA, AafAdsA, AggBdsA and AafBdsA. (C and D) Structural superposition of AggAdsA and AafAdsA (C) and AggBdsA and AafBdsA (D) (stereo view). (E) Topology diagrams. The core structure of AggAdsA, AafAdsA, AggBdsA and AafBdsA is painted in magenta, cyan, green, and pink, respectively. The AggA and AafA Gd donor strands are colored in red and blue, respectively. The loop linking the core structure and donor strand (visible in AggAdsA, AafAdsA and AafBdsA) is shown in orange. Donor strand residues and disulfide bonds are shown as balls and sticks in A. Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms are painted in yellow, red, blue and orange, respectively. Secondary structure elements are labeled in A and B.