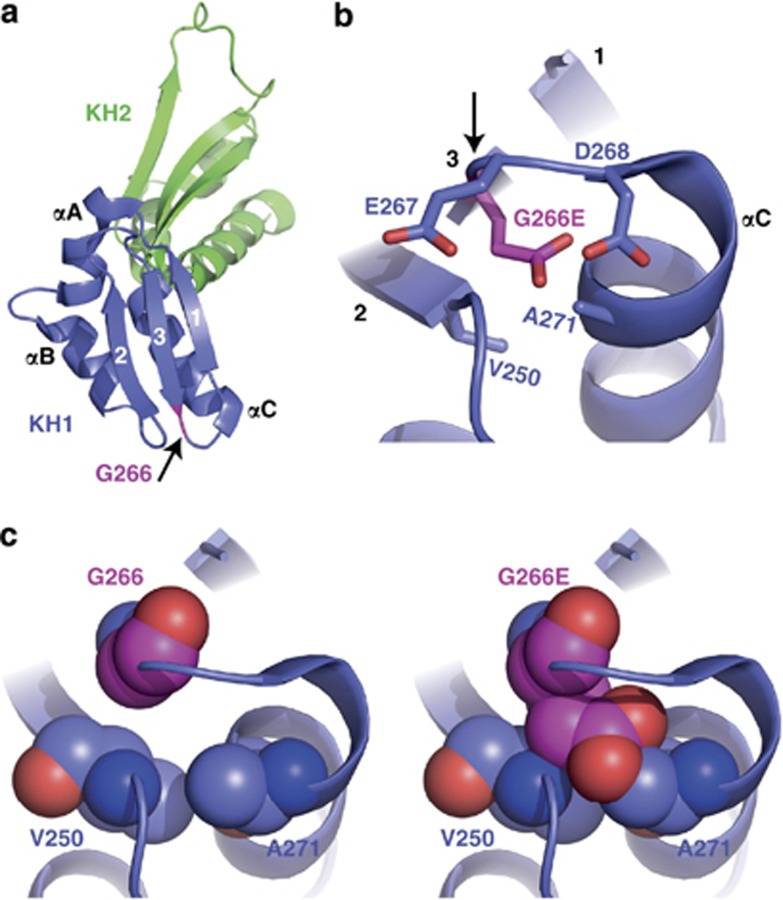
Figure 3.
Structural analysis of mutant G266E-FMRP. (a) Ribbon representation of the FMRP KH1 (blue) and KH2 (green) domains from Protein Data Bank code 2QND. The three β-strands (1, 2, and 3) and three α-helices (αA, αB, and αC) of KH1 are labeled, and the position of Gly266 is highlighted in pink as indicated by the arrow. (b) Stick representation of residues 266–268 showing the close proximity of three negatively charged amino acids when residue 266 is converted from glycine (neutral) to glutamic acid (negative). Arrow points to residue 266. (c) Sphere representations of glycine (left) or glutamic acid (right) at residue 266. There is high probability for glutamic acid to crash into residues V250 and A271 due to the space constraints predicted by this structural model.