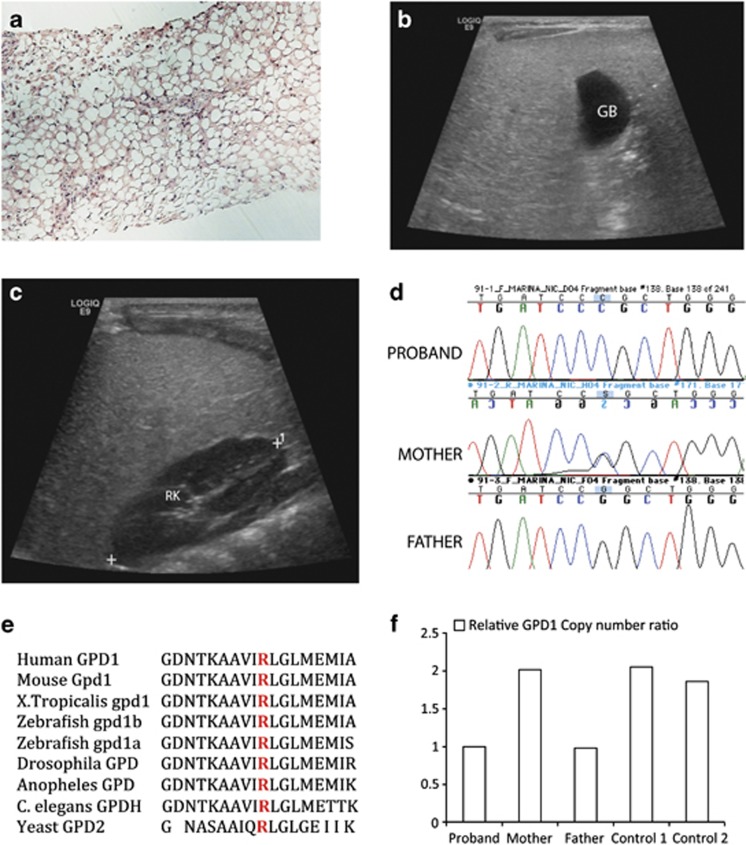
Figure 1.
Radio-pathologic and genetic findings in proband with GPD1 mutation. (a) Liver biopsy: the liver parenchyma shows macro- and microvesicular fatty change on Hematoxylin and Eosin staining (H&E), magnification × 10. (b and c) Ultrasound demonstrates diffuse hyperechogenicity of the liver with a fine granular pattern. In comparison, the gall bladder (GB) (b) and right kidney parenchyma (RK) (c) are hypoechoic. (d) DNA sequence analysis of genomic PCR products illustrates three genotypes for GPD1 c.686G>C seen in the family with proband homozygous, mother heterozygous and father WT for the allele. (e) Altered arginine residue (red) is evolutionarily well conserved in GPD1 and GPD1L proteins in vertebrates and lower organisms including yeast. (f) Relative GPD1 expression levels using copy number assay revealed father and proband to be GPD1 haploinsufficient relative to the mother and two controls.