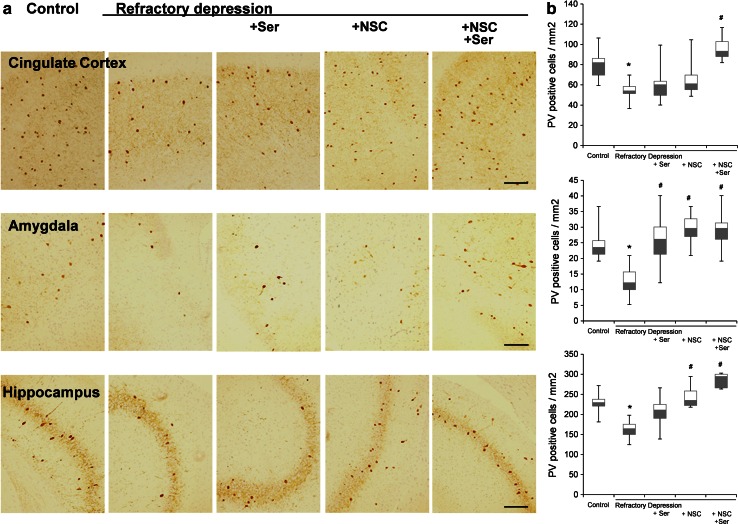
Fig. 4.
Decreased number of PV-positive interneurons and their area-dependent reverses by various treatments. a PV-positive cells were counted in coronal sections from control, refractory depression, refractory depression + Ser, refractory depression + NSCs, and refractory depression + NSCs + Ser treated rats. b Immunohistochemistry with DAB-labeled anti-PV antibody indicated that the amount of PV-positive cells significantly decreased in anterior cingulate cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus in refractory depression model rats (*P < 0.05). In cingulate cortex, combined treatment of NSCs and Ser significantly reversed the reduction of these cells. In amygdala, all three treatments of Ser, NSCs, and NSCs + Ser significantly recovered these reductions. In hippocampus, both treatments of NSCs and combined treatment of NSCs and Ser significantly recovered these reductions. (# P < 0.05). Data represent mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3–4, two sections per rat). Scale bars 100 μm