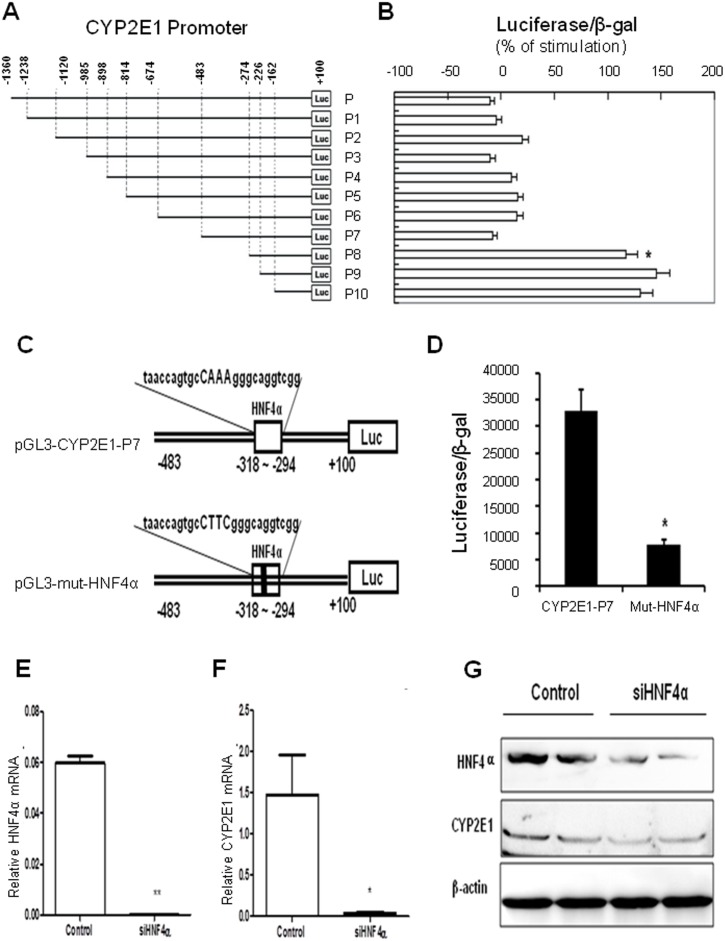
Figure 3. HNF-4α plays a critical role in CYP2E1 gene expression.
(A) A schematic depiction of different human CYP2E1 promoter regions cloned into the pGL3-basic plasmid. The constructs were designated as CPY2E1-P-luc and its various deletion constructs CPY2E1-P1-luc to -P10. (B) Effects of HBx overexpression on promoter activities of different CYP2E1 promoter constructs and identification of a specific promoter region localized at −483∼−274 bp on the CYP2E1 gene 5′-flanking region upstream of the transcription start site which mediates the inhibition effect of HBx to repress CYP2E1 expression. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with one of the CYP2E1 promoter constructs and HBx expression plasmid or control plasmid. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were harvested for determination of relative luciferase activities. Results are expressed as percent of the corresponding control in the absence of HBx expression and represent mean±standard deviation. Results are expressed as percent of the corresponding untreated control cells and represent as mean±standard deviation; *, P<0.001 vs. construct CPY2E1-P7-luc. (C) Schematic representation of the consensus HNF4α binding element and its mutant forms on the human CYP2E1 gene promoter. Site-directed mutagenesis on HNF4α consensus binding was performed, and the mutant constructs were named pGL3-mut-HNF4α; (D) Effects of HNF4α binding site mutation on CYP2E1 promoter activity. (E–F) Effects of silencing HNF4α on endogenous HNF4α and CYP2E1 mRNA expression by real-time PCR, and (G) on their protein expressions by Western Blotting with β-action as internal control.