Figure 3.
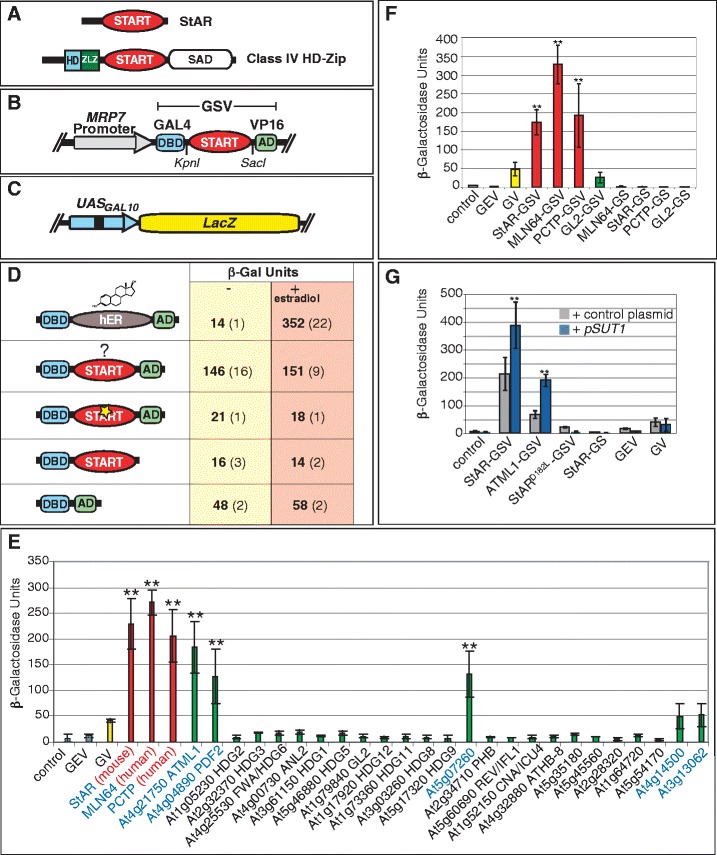
The START domain stimulates transcription factor activity in yeast. (A) Mammalian StAR and a plant-derived HD-Zip transcription factor. (B) GSV synthetic transcription factor. (C) GAL4-DBD binding to UAS from GAL10 drives a LacZ reporter. (D) The START domain stimulates activity of the GV transcription factor. A representative experiment is shown for the START domain derived from mouse StAR. When hER is placed between GAL4-DBD and VP16-AD (GEV), treatment with estradiol (10 μg/ml) leads to increased LacZ activity. START domain activity is unchanged by estradiol treatment. START domain missense mutation (StARD182L) (yellow star) results in loss of activity. Removal of VP16-AD similarly results in loss of activity, and GV that lacks the START domain results in a low level of activity. (E) Three Mammalian START domains (red) and at several Arabidopsis START domains (green) exhibit significant activity levels in comparison to one or more controls: GV (yellow), GEV (grey) and the vector control (pRS314) (grey). (F) The START domain is not a transcriptional AD. Removal of VP16-AD resulted in GS constructs that lack activity. (G) Over-expression of SUT1 results in elevated activity. START domains from mouse StAR or Arabidopsis ATML1 exhibit an increase in GSV activity when co-expressed with the pSUT1 (blue). Asterisks indicate a significant difference over control plasmid (two-tailed t-test, P < 0.0005). Other constructs that do not contain a functional START domain, i.e. StARD182L, GEV and GV, do not display increased activity. In all graphs, error bars indicate standard deviations for two independent transformants in four trials. AD, activation domain; ATML1, Arabidopsis thaliana Meristem Layer 1; DBD, DNA binding domain; GEV, Gal4 DNA binding domain:estrogen receptor: VP16 activation domain; GSV, Gal4 DNA binding domain: START domain: VP16 activation domain; GV, GAL4 DNA binding domain: VP16 activation domain; HD, homeodomain; hER, human estrogen receptor; LacZ, gene for β-galactosidase; MRP7, Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein 7; SAD, START adjacent domain; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; START, StAR-related lipid transfer; SUT1, Sterol Uptake 1; Zip, leucine zipper; ZLZ, Zip-Loop-Zipper (a plant-specific leucine zipper); β-Gal, β-galactosidase.
