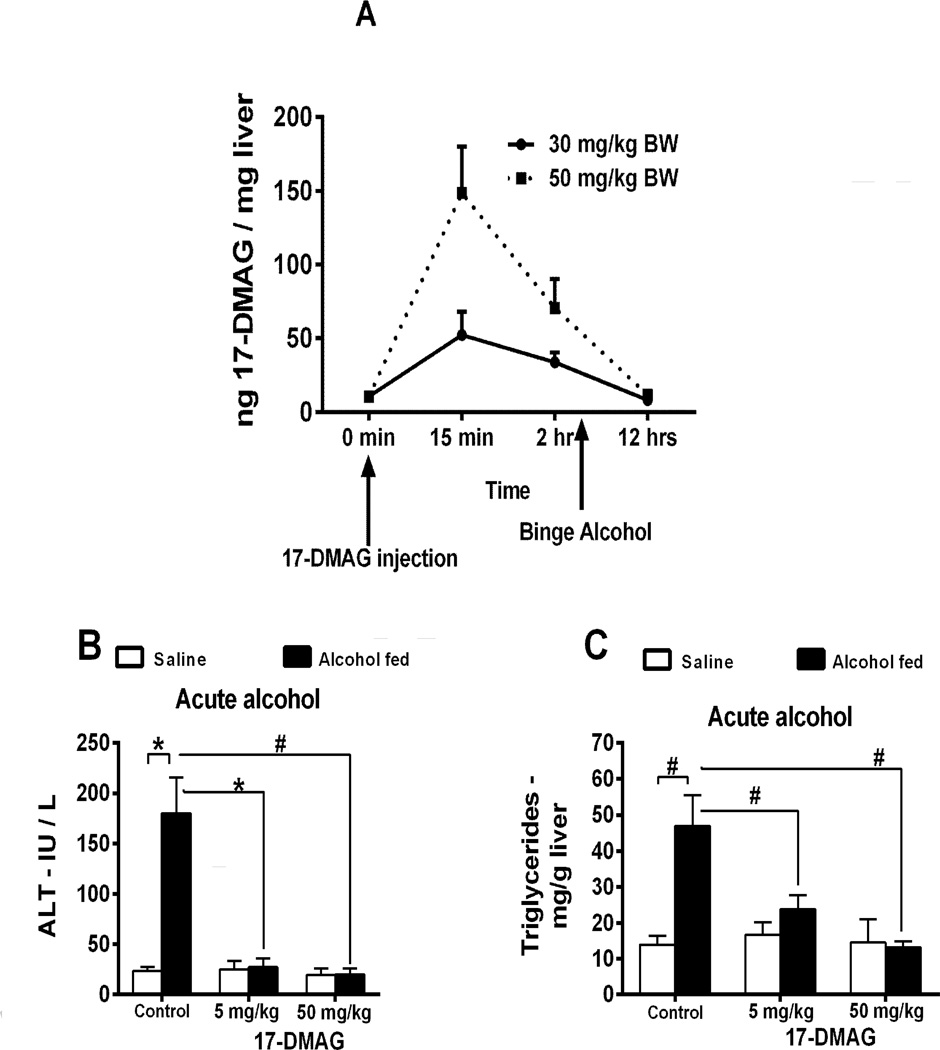
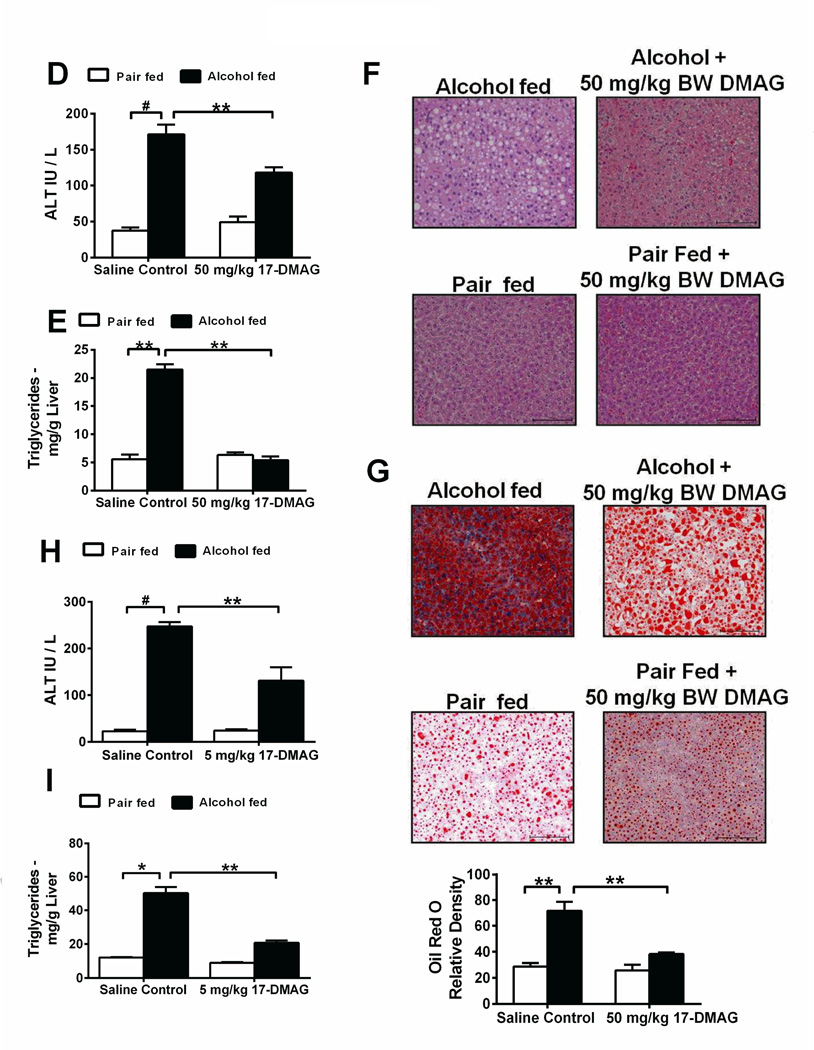
Figure 2. Hsp90 inhibition using 17-DMAG alleviates acute and chronic alcohol induced liver injury.
Bioavailability of 17-DMAG (A) was assayed by LC-MS/MS in liver. Serum ALT (B) and liver triglycerides (C) analyzed in acute alcohol and 17-DMAG administered mice. Serum ALT (D), liver triglycerides (E), histology (F) and Oil Red O staining (G) were investigated in mice fed chronic-binge alcohol and treated with 17-DMAG at the end of the feeding. Bar graph (G) shows relative density of lipids measured using ImageJ software. 17-DMAG administered every alternate day during alcohol feeding and serum ALT (H) and liver triglycerides (I) analyzed. Bars represent mean ± SE, (n=6). **p<0.05, *p<0.0005, #p<0.00005.