Fig. 3.
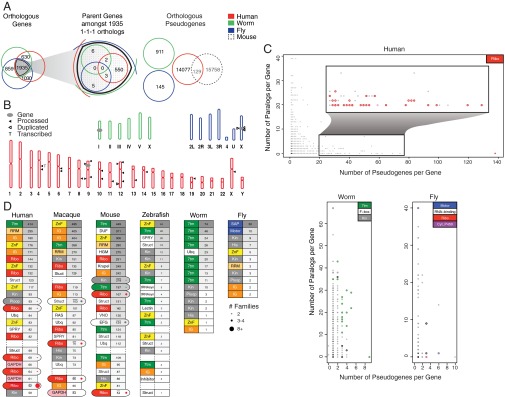
Orthologs, paralogs, and families. (A) Venn diagrams showing the total number of orthologous genes and pseudogenes, in human, worm, and fly. (Right) Pseudogene orthologs between human and mouse. (B) Per chromosome distribution of RpS6 pseudogenes in human, worm, and fly. (C) Comparative distribution of pseudogene and paralogs per gene. (D) Top pseudogene families that give rise to 25% of the total number of pseudogenes in each organism (Left, family type; Right, number of pseudogenes). Oval rows indicate the collapse of two or more consecutive families of the same type. 7tm, G protein-coupled receptors; His, histone; IG, Ig; Kin, kinase; Ploop, P-loop NTPase proteins; Ribo, ribosomal proteins; RRM, RNA recognition motifs; Struct, structural protein; ZnF, Zinc finger proteins (TF); Ubq, ubiquitination proteins; Motor, kinesin motor domain proteins; SAP, SAP domain proteins.
