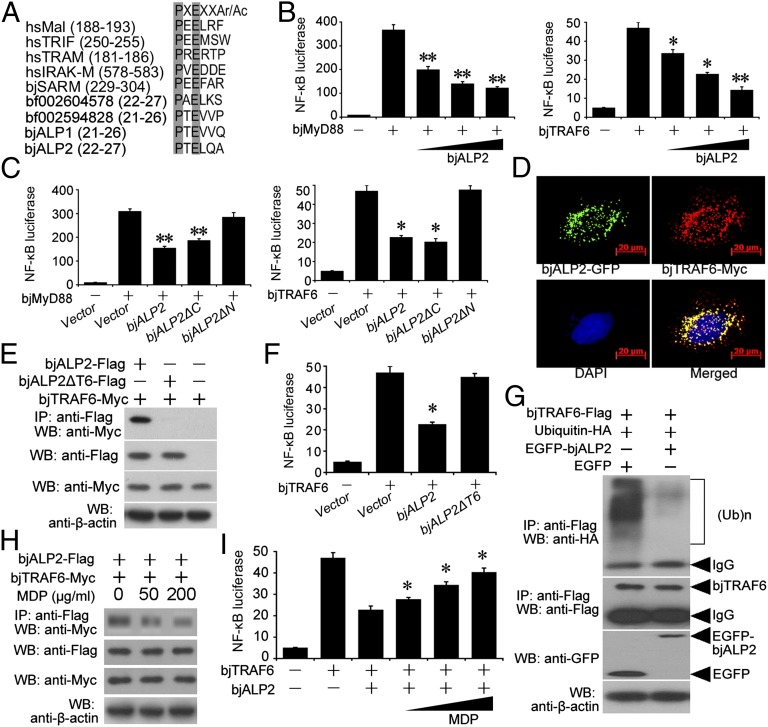
Fig. 6.
BjALP2 interacts with bjTRAF6 via the TRAF6-binding motif and inhibits the ubiquitination of TRAF6 to suppress NF-κB activation. (A) Putative TRAF6-binding motifs identified in amphioxus ALPs. (B) Luciferase reporter assay showing the BjALP2 inhibition of NF-κB activation induced by bjMyD88 and bjTRAF6. (C) The influence of truncated bjALP2 mutants on NF-κB activation as analyzed by luciferase reporter assay. (D) BjALP2 colocalizes with amphioxus TRAF6 in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were cotransfected with EGFP-fused bjALP2 and myc-tagged pCMV-bjTRAF6 and were stained with an anti-myc antibody and an Alexa Fluor 532 secondary antibody. (E) Co-IP assay showing that bjALP2, but not the TRAF6-binding motif-deleted mutant, interacts with amphioxus TRAF6 when overexpressed in 293T cells. (F) Luciferase reporter assay showing that the TRAF6-binding motif-deleted mutant of bjALP2 did not inhibit NF-κB activation. (G) Co-IP assay showing that bjALP2 suppressed the ubiquitination of amphioxus TRAF6 when coexpressed in 293T cells. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (H) Co-IP assay showing that MDP diminished the binding of bjALP2 with bjTRAF6. (I) Luciferase reporter assay showing that MDP relieved the inhibition by bjALP2 of bjTRAF6-induced NF-κB activation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.