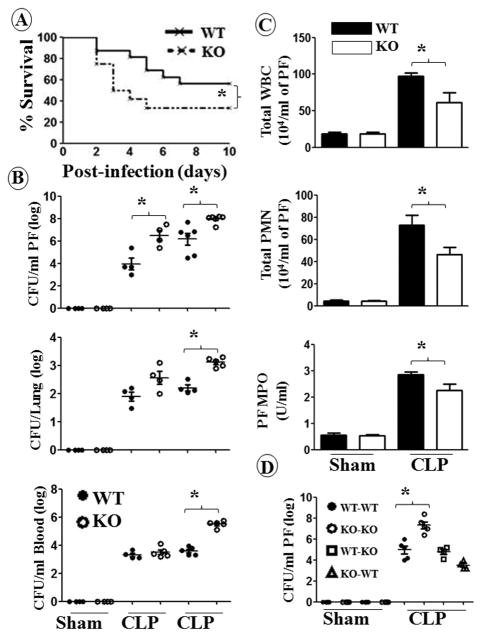
Figure 1. CXCL1 deficient mice are more susceptible to polymicrobial sepsis (PMS) than WT mice and are defective for cellular infiltration and bacterial clearance.
A, Enhanced mortality of cxcl1−/− mice after CLP-induced PMS. cxcl1−/− and WT control mice were subjected to sham or PMS. The survival rates of mice were determined every 12 h until 10 days after PMS. The results are expressed as percent for 20 animals per group. Significance between groups was examined by Wilcoxon rank test.. B, Impaired bacterial clearance in cxcl1−/− mice. The CFUs were examined in peritoneal lavage fluid and blood or the homogenates obtained from lungs of cxcl1−/− as well as WT mice at 6 and 24 h post-PMS. The results are expressed as mean log of CFU/mL (n=5/group). C, cxcl1−/− mice have reduced total WBC and neutrophil accumulation at the peritoneum after PMS, as measured by direct cell counts (for total WBC and neutrophils) or MPO activity (for neutrophil influx). The results are expressed as mean/mL (n=5-8/group). D, Both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells are essential for bacterial clearance. Bone marrow chimeras were generated as described in Methods and show bacterial CFUs at 24 h post-PMS or sham (n=5 mice/group). *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001.