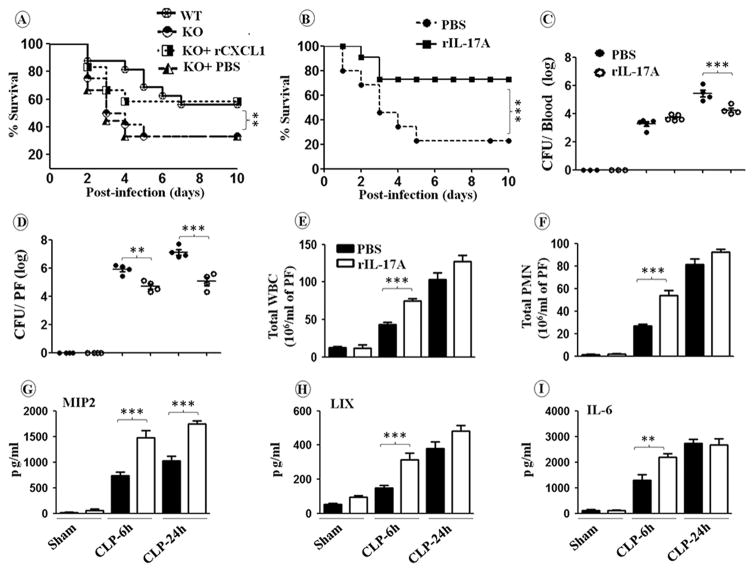
Figure 6. Enhanced mortality, higher bacterial burden, reduced leukocyte recruitment, and attenuated cytokine/chemokine production in peritoneal fluid (PF) are rescued in cxcl1−/− mice following PMS after rCXCL1 or rIL-17A administration.
A-B, cxcl1−/− and WT control mice were subjected to sham surgery or PMS and PBS, rCXCL1 or rIL-17A was immediately injected intraperitoneally. Survival was assessed every 12 h up to 10 days after PMS. The results are expressed as percentage for 20 animals per group. Significance between groups was examined by Wilcoxon rank test. C, Bacterial clearance in cxcl1−/− mice after CLP is rescued by exogenous rIL-17A administration. CFUs were determined in the peritoneal fluid and blood of cxcl1−/− mice mice at 6 and 24 h post-PMS. D, Total WBC and neutrophil accumulation at peritoneum in cxcl1−/− mice following PMS are rescued after administration of rIL-17A. E, Production of cytokine and chemokines production in PF of are rescued after administration of rIL-17A. The results are expressed as mean ± SE (n=5-8/group; *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001).