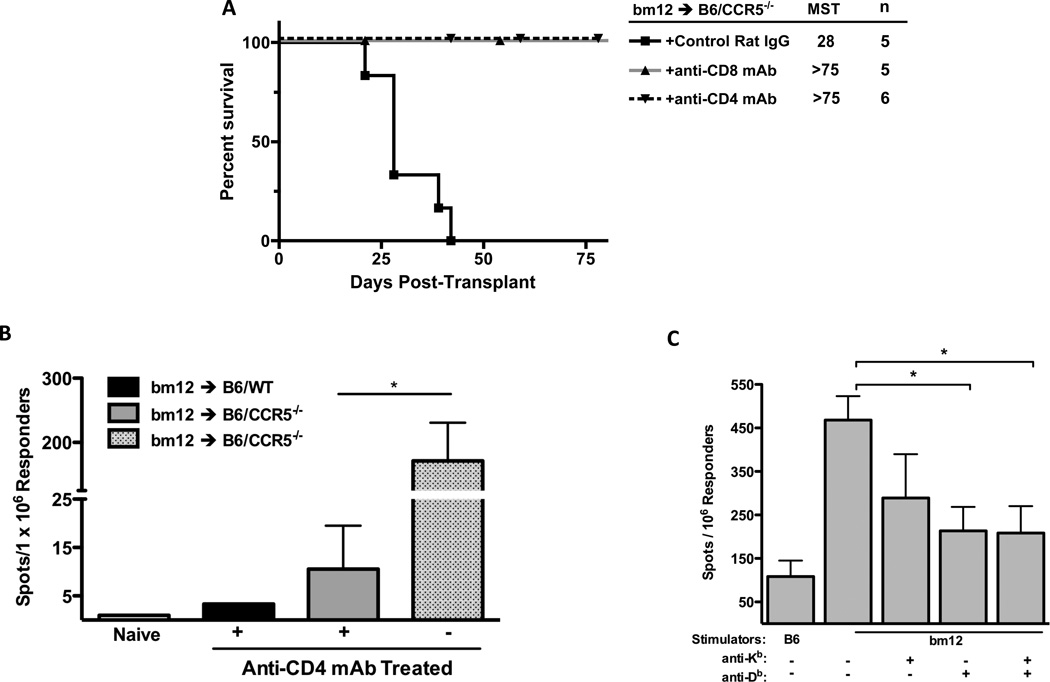
Figure 6.
Rejection of single class II MHC-disparate bm12 renal allografts in B6.CCR5-deficient recipients is dependent on CD4 and CD8 T cells. (A) B6.CCR5−/− mice were treated with 200 µg control rat IgG, anti-CD4 mAb or anti-CD8 mAb on three consecutive days prior to transplantation with a B6.H-2bm12 kidney and allograft survival was monitored. (B) Groups of wild type C57Bl/6 and B6.CCR5-deficient mice received bm12 renal allografts, with the indicated groups depleted of CD4 T cells by treating with anti-CD4 mAb prior to the transplant. On day 14 post-transplant, CD8 T cells were purified from each of the recipient spleens and the frequency of bm12 donor-reactive CD8 T cells producing IFN-γ was quantified by ELISPOT assay. The results indicate the mean number of spots for splenic CD8 T cells from 4 individual mice per group ± SEM. *p < 0.05. (C) Groups of B6.CCR5−/− mice received bm12 renal allografts. On day 20 post-transplant, CD8 T cells were purified from each of the recipient spleens and the frequency of CD8 T cells producing IFN-γ during culture with syngeneic C57BL/6 or bm12 stimulator cells was quantified by ELISPOT assay. In the indicated cultures, 20 µg of anti-Kb and/or anti-Db mAb was added at the initiation of the ELISPOT culture. The results indicate the mean number of spots for splenic CD8 T cells from 4 individual mice per group in each of the stimulation cultures ± SEM. *p < 0.05.