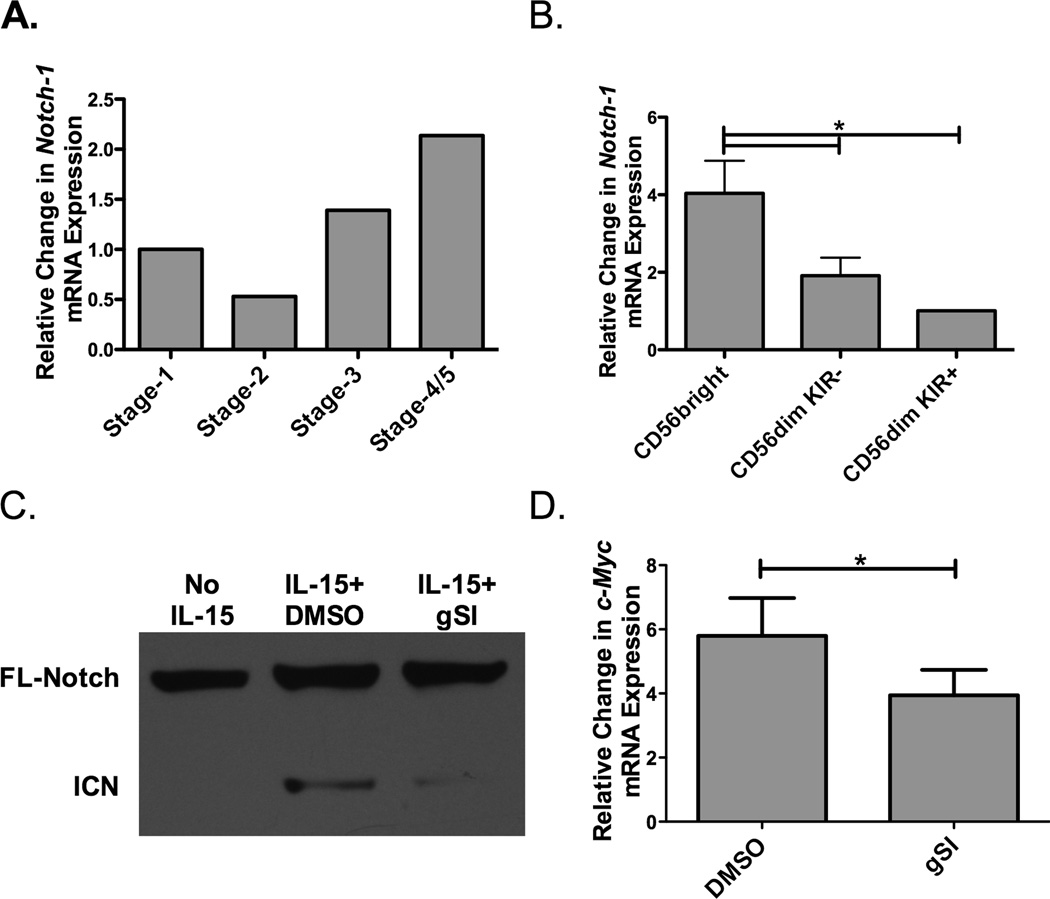
Figure 1. Regulation of Notch expression and signaling on NK cells.
A) Pooled umbilical cord blood (UCB, n=5) was used as a source of hematopoietic progenitors and Notch-1 transcript expression (normalized to GAPDH) was determined at different stages of NK cell development (Stage 1-CD34+CD117−CD56−, Stage 2-CD34+CD117+CD56−, Stage 3-CD34−CD117+CD56−CD94/CD16−, and Stage 4/5-CD34−CD117−CD56+CD94/CD16+). (B) Peripheral blood NK cells were first enriched utilizing magnetic beads and then sorted based on CD56 expression and presence of KIR. Notch-1 transcript expression (normalized to GAPDH) was determined in CD56brightKIR−, CD56dimKIR−, and CD56dimKIR+ NK cells (n = 4). (C) Representative Western Blot of full length (FL) and intercellular Notch-1 (ICN) protein in enriched adult NK cells after overnight culture with no cytokine or 10 ng/ml of IL-15 in the presence of either DMSO or 20 µM γ-secretase inhibitor (gSI) (n = 6). (D) c-Myc transcript expression (normalized to 18s) in adult NK cells after 3 days of stimulation with 10 ng/ml of IL-15 in the presence of either DMSO or 20 µM gSI (n=6).