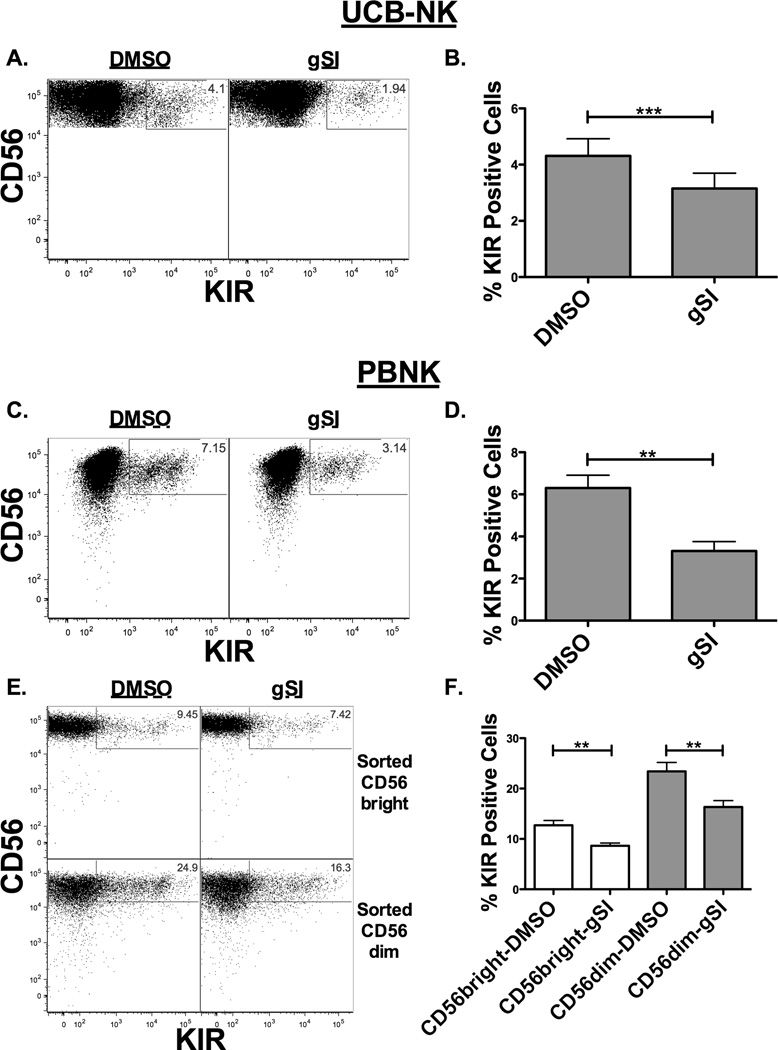
Figure 2. Notch signaling blockade results in reduced KIR expression.
KIR expression was evaluated on developing NK cells or adult NK cells after inhibition of the Notch pathway. (A–B) UCB progenitors were differentiated into NK cells by co-culture with EL08-1D2 stroma and cytokines for 21 days, harvested and cultured for an additional 7 days in 10 ng/ml IL-15 with DMSO or 20 uM gSI. Flow plots (A) and aggregate data (B) showing KIR expression on CD56+CD3− NK cells (n = 14). (C) Representative dot plot and (D) aggregate data of fresh sorted adult donor CD56+KIR− NK cells cultured for 7 days in 10 ng/ml IL-15 with DMSO or 20 uM gSI showing KIR expression on CD56+CD3− NK cells (n = 4). (E) Representative dot plot and (F) aggregate data of sorted CD56brightKIR− (top panels and open bars) or CD56dimKIR− (bottom panels and filled bars) NK cells cultured for 7 days in 10 ng/ml IL-15 with DMSO or 20 uM gSI showing KIR expression on CD56+CD3− NK cells (n = 5). On panel (F) CD56bright and CD56dim paired comparison were done separately as these represent different experiments.