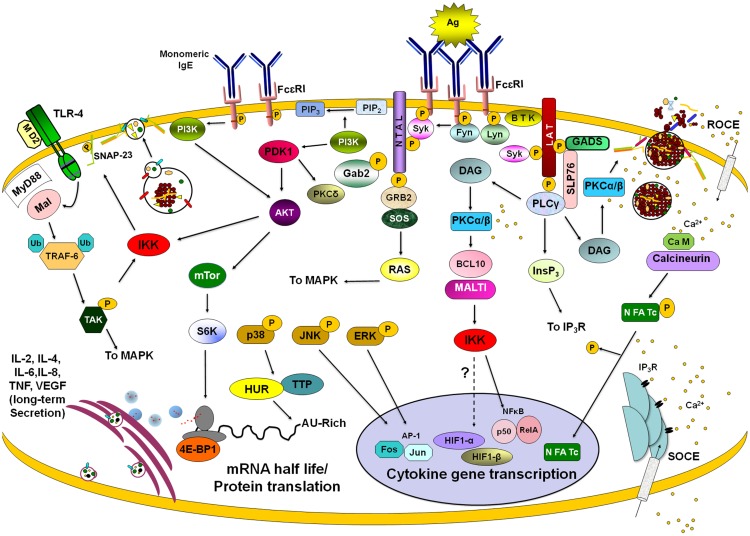
Figure 4.
Late signaling events in de novo cytokine/chemokine production. Stimulation of different membrane receptors lead to the activation of transcription factors, modulators of mRNA turnover, and effectors of ribosome activity that provoke long-lasting secretion of lymphokines in mast cells. After FcεRI triggering with IgE/antigen (Ag) complexes, Lyn and Fyn tyrosine kinases become activated and phosphorylate ITAMs from β and γ chains of the receptor. Further activation of Syk kinase leads to the phosphorylation of a number of adapters (such as LAT and NTAL) and enzymes (such as BTK and PLCγ). Enzymes and adapters form different macromolecular aggregates leading to the activation of different signaling pathways. PLCγ activation is connected with PKCα/β-dependent events through the generation of DAG and IP3. PKCα/β connect FcεRI triggering with IKK activation and IκB degradation, leading to nuclear translocation of NFκB. IP3-sensitive calcium release from intracellular stores lead to the activation of a store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). IgE/Ag stimulation initiates also a receptor-operated Ca2+ entry (ROCE). Calcium increase allows calcineurin-dependent dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NFAT. On the other hand, Fyn-PI3K pathway leads to the activation of IKK and NFκB-dependent transcription but also triggers AKT, which controls mTor kinase and the initiation of protein translation by S6K and 4E-BP1. Activation of MAPK provokes the activation of AP-1 transcription factor but also modifies cytokine mRNA turnover through the modulation of mRNA-binding proteins such as HUR and Tristetraprolin (TTP). Binding of monomeric IgE to FcεRI induces mTor-dependent changes on 4E-BP1 phosphorylation leading to modifications on cap-dependent protein translation. Stimulation of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) leads to NFκB-mediated transcription by the MyD88/Mal-dependent pathway, which renders IKK activation after the TRAF-6/TAK1 axis. IKK, either activated by FcεRI or TLR4 receptors, phosphorylates SNAP-23 facilitating secretion. Also, IKK triggering (together with some calcium-dependent signals) modulates HIF1-α-dependent transcription. Once translated, cytokines and angiogenic factors are secreted for variable periods of time utilizing specific vesicle carriers. See text for details.