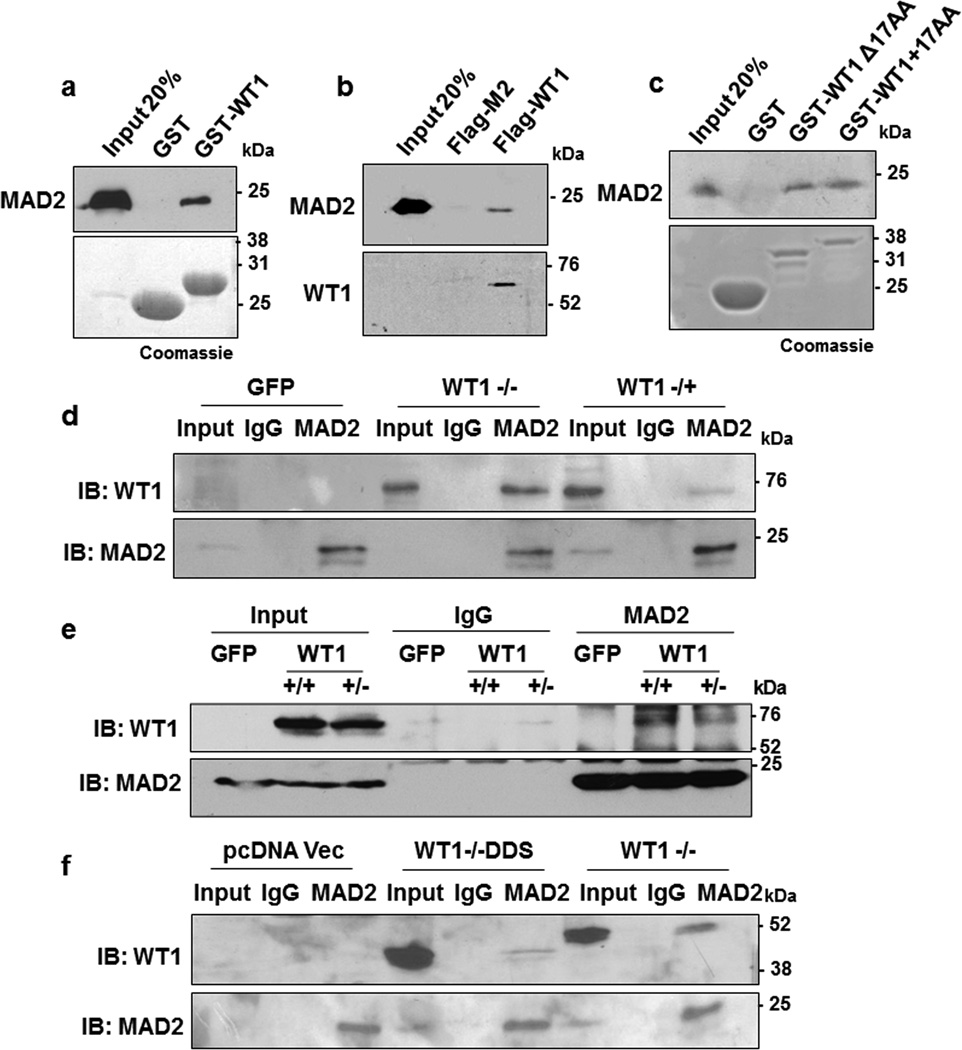
Figure 1. WT1 interacts with MAD2.
(a) In vitro interaction assay was performed with either GST-WT1 (residues 245–297) or GST in the presence of full length His-MAD2. The interaction was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-MAD2 antibody. Bound proteins were also resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (b) In vitro pulldown assay was also performed with either Flag-M2 magnetic beads alone or incubated with full length Flag-tagged WT1 protein in presence of His-MAD2. The interaction was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-WT1 and anti-MAD2 antibodies (c) GST-interaction assay was carried out with WT1 containing the 17 amino acid insertion (residues 180-297, +17AA) or lacking it (residues 180-297, Δ17 AA) with His-MAD2. The interaction was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-MAD2 antibody. Bound proteins were also resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (d) HeLa cells were transfected with GFP Vector, full length GFP-WT1 (−/−) or GFP-WT1 (−/+) isoforms and 48 hours later whole cell extracts were prepared followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-MAD2 antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were probed with anti-WT1 antibody. Blotting with anti-MAD2 antibody was performed as a control. (e) The MAD2 interaction with ectopically expressed GFP tagged full length WT1 (+/+) and WT1 (+/−) isoforms was analyzed as in part d (f) HeLa cells were transfected with pcDNA vector, pcDNA driving expression of WT1−/−DDS (R394X) or wild type WT1−/− followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-MAD2 antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were probed with anti-WT1 antibodies. Blotting with anti-MAD2 antibodies was performed as a control.