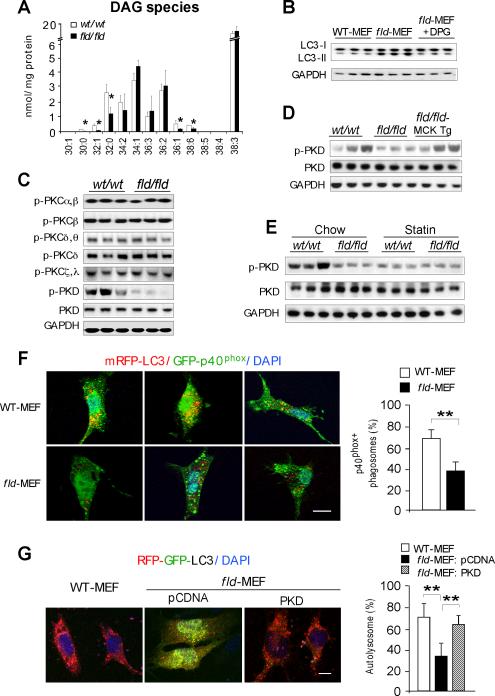
Figure 5. Lipin-1 Deficiency Inhibits the PKD-Vps34 Pathway in Autophagy Clearance.
(A) Diacylglycerol quantification by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in hindlimb muscle of wild-type (wt/wt) and fld/fld mice (n = 3). The molecular species of diacylglycerol in muscle are represented as the number of carbons:number of double bonds. *, p < 0.05.
(B) Immunoblot showing addition of 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycerol (DPG, 100 μM) increases LC3-II degradation in starved fld-MEFs.
(C) Immunoblot assessment of the activity of muscle protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms and protein kinase D (PKD) with the indicated antibodies.
(D) Muscle lipin-1 transgene rescues PKD activity in fld/fld muscle in mice under basal conditions.
(E) Immunoblot analysis of PKD activity in muscle of mice under basal (Chow) and statin treated conditions.
(F) Analysis of Vps34 activity in autophagy by co-localization of PtIns3P binding probe GFP-p40phox and RFP-LC3 in primary MEFs after starvation. Left, representative confocal microscopy images, with PtIns3P presence in autophagosomes indicated by yellow puncta. Right, percentage of autophagosomes with visible yellow puncta, indicating presence of PtIns3P. n = 80 cells per group. Scale bars in panels (F) and (G) correspond to 10μm.
(G) Expression of active PKD restores autophagy flux in fld-MEFs. Constitutively active PKD (S738E/742E) and RFP-GFP-LC3 reporter were co-transfected into primary MEFs. Left, representative confocal microscopy images. Red puncta indicate formation of autolysosomes. Right, percentage of LC3 reporter present in autolysosomes. n = 80 cells per group. *, p < 0.05.