Figure 2. ASP3026 reduces the tyrosine kinase activity of NPM-ALK, downregulates the phosphorylation of NPM-ALK and target proteins, and induces biochemical effects consistent with apoptosis.
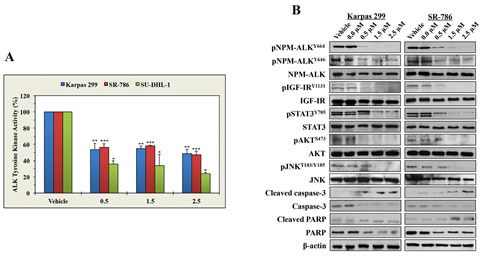
(A) ASP3026 induced a marked decrease in NPM-ALK tyrosine kinase activity in the lymphoma cells (*: P < 0.01, **: P < 0.001, ***: P < 0.0001 compared with control cells treated with vehicle). Results shown are means ± SE of 3 experiments. (B) ASP3026 decreased the phosphorylation of NPM-ALK at 2 different tyrosine residues: Y646 and Y664. Also, treatment with ASP3026 was associated with downregulation of the phosphorylation of the NPM-ALK target proteins IGF-IR, STAT3, AKT, and JNK. Changes in the basal levels of these proteins were not detected. The occurrence of apoptosis was biochemically supported by the increase in cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP and the simultaneous decrease in non-cleaved caspase-3 and non-cleared PARP levels. β-Actin indicates equal loading of the proteins.
