Figure 3. ASP3026 overcomes the resistance to crizotinib in NPM-ALK+ ALCL.
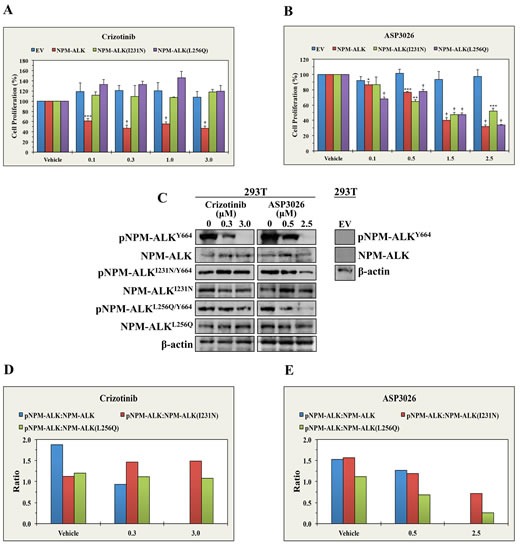
(A) Whereas crizotinib induced significant decrease in the proliferation of 293T cells transiently transfected with NPM-ALK, it failed to induce similar effects in the cells transfected with EV, NPM-ALKI231N or NPM-ALKL256Q. (B) ASP3026 successfully decreased the proliferation of 293T cells transfected with NPM-ALK, NPM-ALKI231N or NPM-ALKL256Q (*: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, †: P < 0.0001). No effects were seen when control 293T cells transfected with EV were treated with ASP3026. Results represent the means ± SE of 3 experiments. (C) The left panel shows that crizotinib decreased the phosphorylation of NPM-ALK transfected in 293T cells, but not the phosphorylation of NPM-ALKI231N or NPM-ALKL256Q. At the other hand, ASP3026 reduced the phosphorylation of the three constructs. The levels of non-phosphorylated NPM-ALK constructs and β-actin support equal protein loading. The right panel illustrates lack of NPM-ALK/pNPM-ALK protein expression in 293T cells transfected with EV. (D) Densitometric analysis depicting the ratio of pNPM-ALK Western blot bands to their corresponding NPM-ALK bands is shown. The results illustrate that crizotinib induced remarkable downregulation of pNPM-ALK in 293T cells transfected with NPM-ALK but not in 293T cells transfected with crizotinib-resistant NPM-ALK mutants. (E) Furthermore, the densitometric analysis also shows that treatment with ASP3026 caused concentration-dependent decrease in pNPM-ALK levels in cells transfected with NPM-ALK, NPM-ALKI231N or NPM-ALKL256Q.
