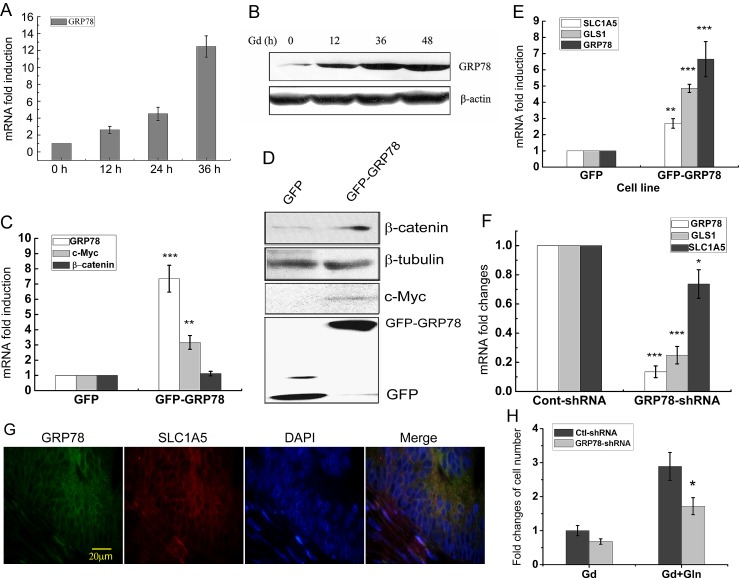
Figure 3. Glucose deprivation-induced GRP78 elevates β-catenin protein level.
(A) Relative mRNA levels of GRP78 in DLD1 cells at the indicated time points following Gd treatment. (B) Western blots of GRP78 in DLD1 cells exposed to Gd for 0, 12, 24 and 36 h. (C) Relative mRNA levels of GRP78, c-Myc and β-catenin in GRP78 overexpressing DLD1 cells. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs GFP. (D) Western blots of c-Myc, β-catenin and GFP in GRP78 overexpressing DLD1 cells. (E) Relative mRNA levels of GRP78, GLS1 and SLC1A5 in GRP78 overexpressing DLD1 cells. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs GFP. (F) Relative mRNA levels of GRP78, GLS1 and SLC1A5 in GRP78 knockdown DLD1 cells. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 vs Cont-shRNA. (G) Fluorescent immunohistochemical demonstration of GRP78 and SLC1A5 in a 5-μm paraffin-embedded section. (H) DLD1 cells were transfected with either Ctrl-shRNA and GRP78-shRNA and subjected to growth under Gd conditions with or without glutamine for 24 h. The cell number changes were examined by MTT assay. *p<0.05 vs Ctrl-shRNA.