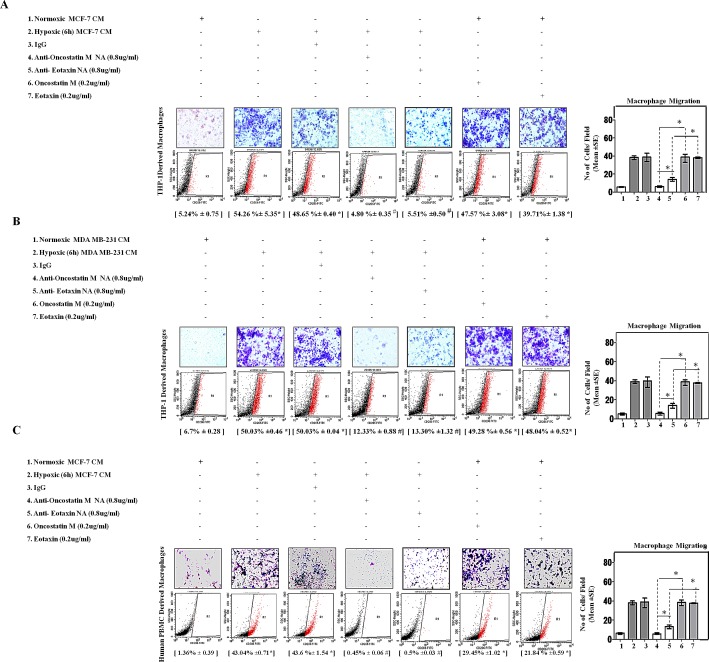
Fig.5. Neutralizing Antibody Mediated Blockade of OncostatinM and Eotaxin Function Prevented Macrophage Chemotaxis and their M2-Polarization.
THP-1 derived macrophages or Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (h-PBMCs) derived macrophages were incubated with conditioned media from hypoxia primed (6hrs) or normoxic breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) CM for 24 hrs in absence or presence of anti-Oncostatin M/anti-Eotaxin neutralizing antibodies or recombinant Oncostatin M/Eotaxin respectively. Thereafter macrophage migration and phenotype switching was evaluated using Geimsa/DAPI staining and flowcytometry respectively. Representative giemsa-staining photomicrographs and Flow cytometry data depicting blockade of directional migration and M2-polarization of THP-1 derived macrophages (A-B) or Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (h-PBMCs) derived macrophages (C) towards hypoxia primed breast cancer cell CM in presence of anti-oncostatin M or Eotaxin neutralizing antibody. Addition of recombinant human Oncostatin M or Eotaxin to normoxic breast cancer cells CM potentiated directional migration and M2-polarization of THP-1 derived macrophages/Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (h-PBMCs) derived macrophages. Quantification of macrophage migration chemotaxis was done by DAPI staining of migrated macrophages followed by counting of nuclei in five different fields of three replica wells. Numbers in parenthesis represent % M2-macrophage count obtained during flow cytometric analysis of three replica sets. Data presented as Mean±SEM; n=5; Symbols indicate statistical significance at p < 0.05 (*-#). Differences between values with matching symbol notation are statistically insignificant.