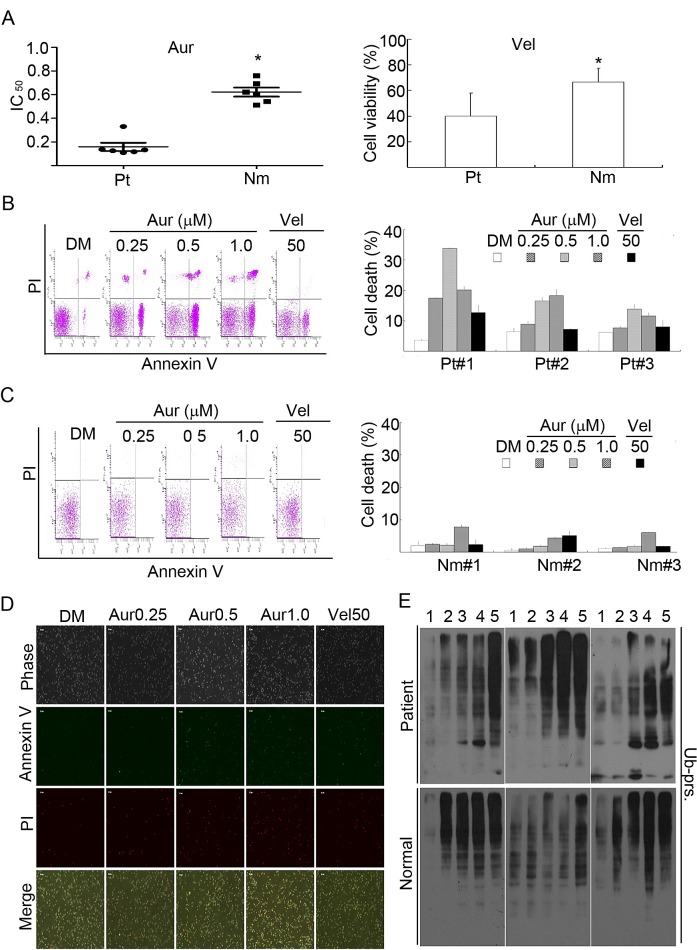
Figure 8. Aur inhibits the proteasome and specifically induces cytotoxicity in cancer cells from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients.
(A) Cancer cells from 6 AML patients (Pt) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 6 healthy volunteers (Nm) were treated with Aur at the indicated doses or with Vel (50 nM) for 24 h and the cell viability was detected by the MTS assay. The scatter plot of the IC50 values in each group was shown (A, left). *P<0.05, versus patients. Cell viability with Vel treatment in each group was shown (A, right). Mean±SD (n=3). *P<0.05, versus AML patients. (B, C) Cancer cells from 3 AML patients or the peripheral mononuclear cells from 3 normal human individuals were incubated with Aur at the indicated doses or with Vel (50 nM) for 12 h. Cell death was analyzed by flow cytometry. The typical images from flow cytometry were shown in (B, C, left) and cell death were summarized in (B, C, right). Mean±SD (n=3). (D) As treated in (B, C), cancer cells from AML patients were treated with Aur or Vel for 15 h, then cells were stained with Annexin V/PI and imaged under a fluorescent microscope. The phase contrast and fluorescent images were taken and merged. Scale bar=50 μm. (E) AML cancer cells and human peripheral mononuclear cells were treated with Aur or Vel for 6 h followed by detecting ubiquitinated proteins with western blot analyses. Western blot images of cells from 3 individuals of each group are shown. At the top of the panel, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 denote control, Aur (0.25, 0.5, 1.0 μM), and Vel (50 nM), respectively.