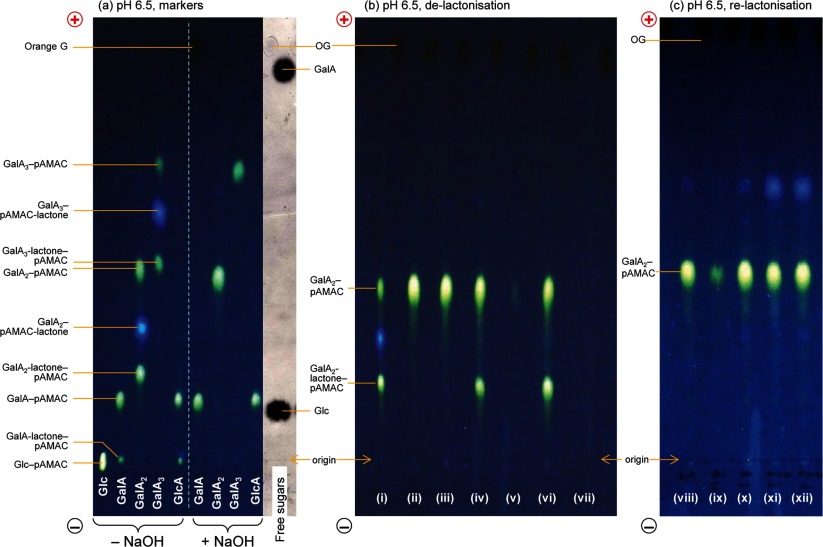
Figure 4. De-lactonization and re-lactonization of pAMAC-labelled oligogalacturonides.
(a) Five reducing sugars (glucose, galacturonic acid, galacturono-biose and -triose and glucuronic acid) were treated with AMAC followed by acetone. The sugar–pAMAC products were analysed by electrophoresis at pH 6.5, both directly (−NaOH) and, in the case of the acidic sugars, after de-lactonization (+NaOH). (b) (i) Crude GalA2–pAMAC (a mixture containing the fully anionic form and two putative lactones); (ii) as (i) but de-lactonized with NaOH and loaded for electrophoresis immediately after neutralization; (iii) as (i) but de-lactonized with NaOH, neutralized, stored 24 h as a solution at 4°C, and then loaded; (iv–vii) as (i) but de-lactonized with NaOH, acidified to pH <1 with HCl to promote re-lactonization, then re-isolated on C18 columns eluted either with (iv) 40% methanol followed by (v) 100% methanol, or with (vi) 40% acetone followed by (vii) 100% acetone. (c) Samples of de-lactonized GalA2–pAMAC were dried from various solvents, then briefly treated at pH 13 with NaOH, neutralized, and loaded for electrophoresis. (viii) Marker of authentic de-lactonized GalA2–pAMAC; (ix) control (in PyAW, 1:1:98 by vol., not dried); (x) dried from PyAW (1:1:98 by vol.); (xi) dried from PyAW (1:1:1 by vol.) containing 15% formic acid; (xii) dried from 15% formic acid in deionized water. The non-dried sample required large amounts of NaOH for raising the pH and therefore only a portion of it was loaded. In all cases, paper electrophoresis was at pH 6.5. Fluorescent spots were visualized under 254-nm UV. Orange G (OG) is an anionic marker (dark spot under UV). The free sugars shown in (a), stained with AgNO3 and scanned under white light, act as markers.