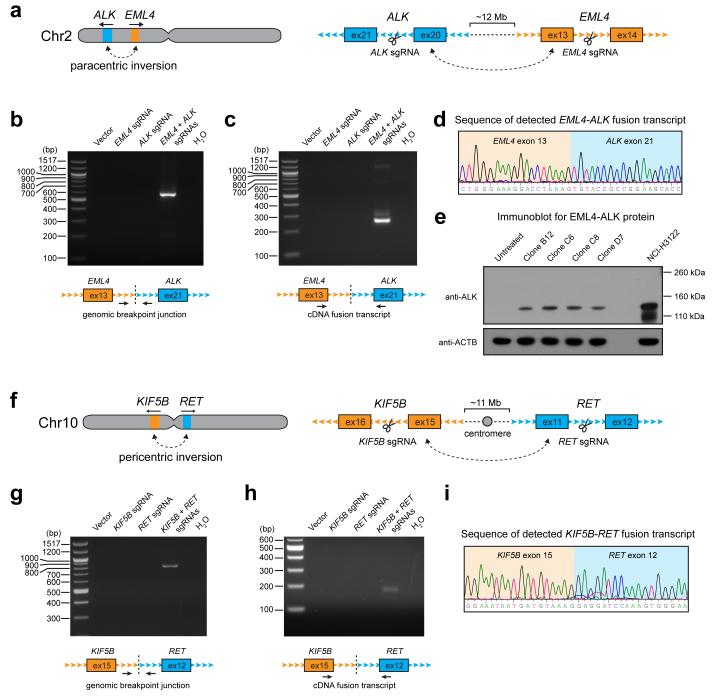
Figure 2. Cas9 can be targeted to generate paracentric and pericentric intrachromosomal inversions.
a) The EML4-ALK rearrangement results from a paracentric inversion in chromosome 2. Shown are the intronic sites where Cas9 was targeted. b-c) PCR detection of the EML4-ALK b) genomic breakpoint junction and c) fusion transcript from HEK 293T cells in which Cas9 was expressed with no sgRNA (vector), EML4 sgRNA alone, ALK sgRNA alone, or both EML4 and ALK sgRNAs. d) Sequence chromatogram of the detected EML4-ALK fusion transcript from cells in which Cas9 and both EML4 and ALK sgRNAs were expressed. e) Western blot for EML4-ALK protein expression in single clones of 293T cells which were untreated, or in which Cas9 and both EML4 and ALK sgRNAs were expressed. NCIH3122 cells are shown as a positive control. f) The KIF5B-RET rearrangement results from a pericentric inversion in chromosome 10. Shown are the intronic sites where Cas9 was targeted. g-h) PCR detection of the KIF5B-RET g) genomic breakpoint junction and h) fusion transcript from HEK 293T cells in which Cas9 was expressed with no sgRNA (vector), KIF5B sgRNA alone, RET sgRNA alone, or both KIF5B and RET sgRNAs. i) Sequence chromatogram of the detected KIF5B-RET fusion transcript from cells in which Cas9 and both KIF5B and RET sgRNAs were expressed. Data shown are representative results from a total of three independent experiments.