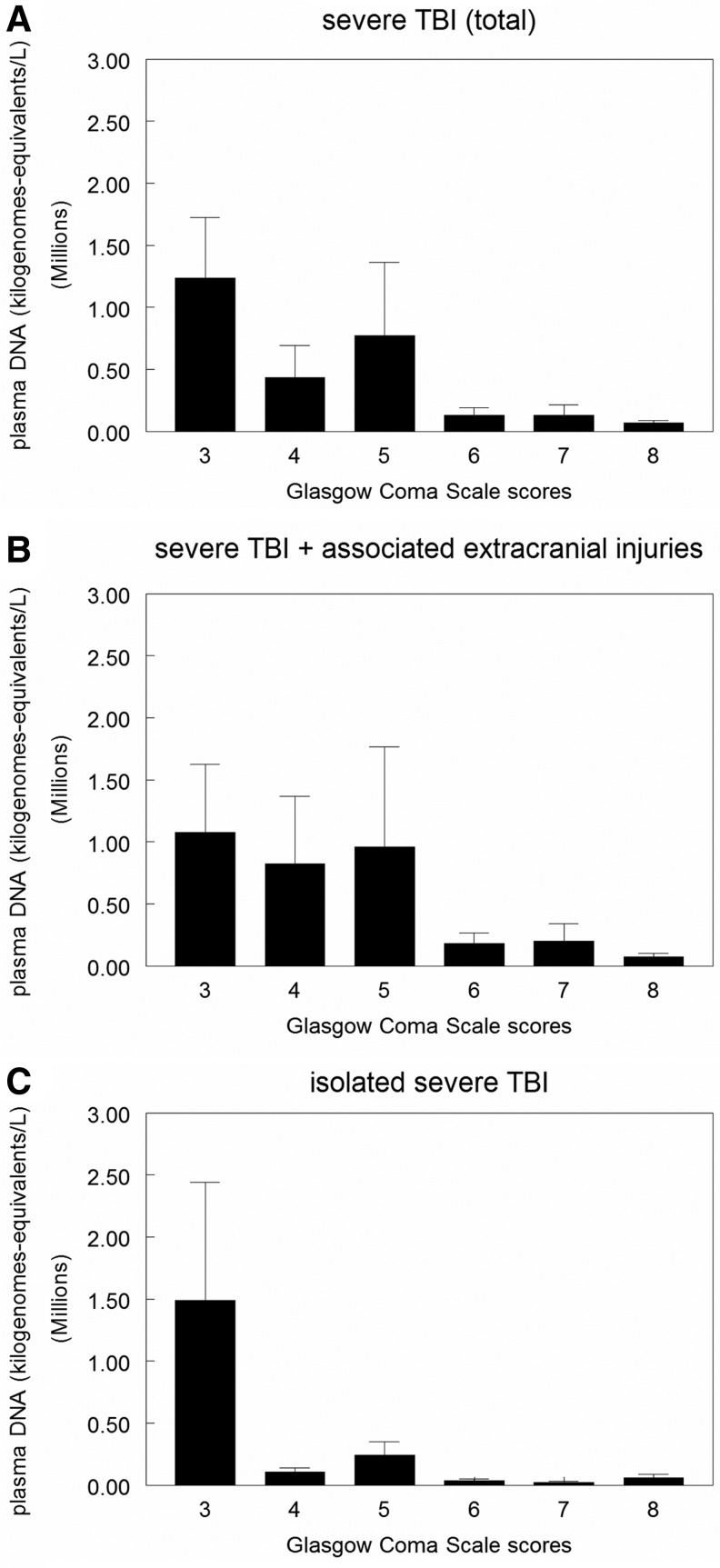
FIG. 2.
Plasma DNA concentrations and hospital admission Glasgow Coma Scale scores in severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) persons stratified by the type of TBI lesion. In (A), data represent correlation between plasma DNA concentrations and hospital admission GCS scores in all persons with severe TBI (n=188). There was a significant correlation between higher DNA levels and lower GCS scores (p=0.001). In (B), data represent correlation between plasma DNA concentrations and hospital admission GCS scores in the group with severe TBI associated with extracranial lesions (n=110). There was a significant correlation between higher DNA levels and lower GCS scores (p=0.003). In (C), data represent correlation between plasma DNA concentrations and hospital admission GCS scores in the isolated severe TBI group (n=78). There was a significant correlation between higher DNA levels and lower GCS scores (p=0.004). Data are expressed as mean±S.E.M.