Figure 1. Kinetic studies on the inhibition of alkyl benzoquinones in glutaminases.
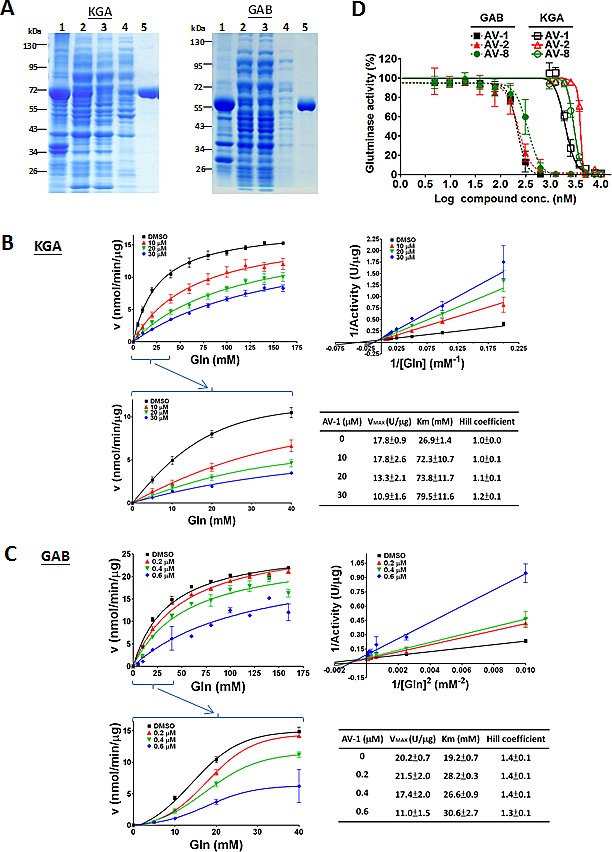
(A) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)pLysS harboring pET28a(+)-KGA or pET28a(+)-GAB was propagated in Luria-Bertani broth medium in the presence of kanamycin, from which KGA or GAB protein expression was induced by 0.5 mM IPTG. The resultant cell lysate was sonicated and centrifugated for fractions of cell pellet (lane 1) and supernatant (lane 2). The supernatant was passed through an affinity column (HisTrapTM HP) and the flow-through was shown in lane 3, as well as the washes with 100 mM and 150 mM of imidazole for KGA(left panel) or 50 mM of imidazole for GAB(right panel) were shown in lane 4. Lane 5 shown was the eluent with 500 mM of imidazole for KGA(left panel) or 200 mM of imidazole for GAB(right panel). Molecular markers were indicated as kDa. (B) Inhibition mode of active alkyl benzoquinone AV-1 for KGA in the absence of phosphate. (C) Inhibition mode of active alkyl benzoquinone AV-1 for GAB in the absence of phosphate. The Cheng-Prusoff equation, Ki=IC50/(1+[S]/Km), was used to calculate Ki values of AV-1 for KGA=1.20±0.06μM and GAB=0.14±0.01μM. (D) Dose dependent inhibition of alkyl benzoquinones against the purified recombinant KGA and GAB in the absence of phosphate.
