Figure 7. Model for how H3K27me3 and H2AK119ub epigenetic signatures modulate DNA methylation patterns.
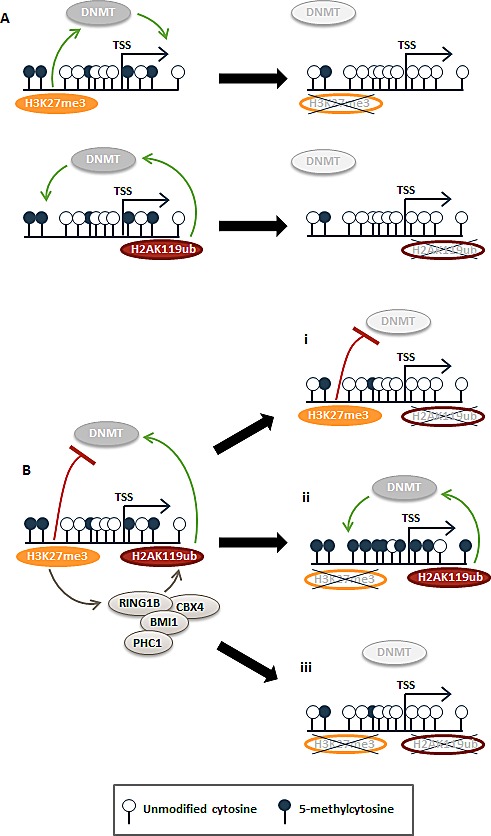
(A) Two distinct subsets of genes were hypomethylated in the single siEED or siRNF2 knockdown conditions. We propose that these are loci in which PRC1 and PRC2 function independently of one another to influence DNA methylation. In the absence of PRC1 or PRC2, these loci become hypomethylated. (B) At another subset of genes, PRC2 and PRC1 act in concert to create a metastable epigenetic state. At these loci, H3K27me3 recruits PRC1 to deposit H2AK119ub. Together these marks establish opposing influences on DNA methylation: H2AK119ub promotes DNA methylation, presumably via DNMT recruitment, but H3K27me3 inhibits DNMT recruitment. With depletion of H2AK119ub, low levels of DNA methylation/DNMT recruitment are lost (i). If H3K27me3 is depleted at previously H3K27me3-marked loci, H2AK119ub remains unrestrained and promotes enrichment of DNA methylation (ii). In the event that both H3K27me3 and H2AK119ub are depleted, recruitment of DNMTs is reduced or lost.
