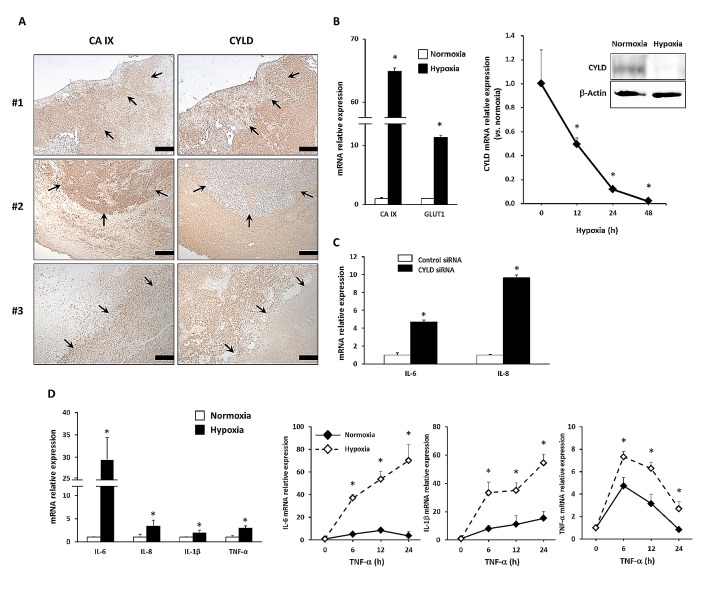
Figure 1. Effects of hypoxia on expression of CYLD and proinflammatory cytokines in GBM cells.
(A) Immunohistochemical analysis with anti-CYLD and anti-CA IX antibodies in GBM tissues. In representative photomicrographs from 3 GBM cases, arrows indicate areas with high CA IX and low CYLD expression. Scale bars indicate 500 μm. (B) U87MG cells were incubated under hypoxic conditions, after which mRNA expression of hypoxic markers (left panel) and CYLD mRNA (right panel) were determined via qPCR. CYLD protein expression was determined by using Western blotting 24 h after hypoxic culture (right panel). * P< 0.05. (C) Expression of IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA was determined via qPCR after CYLD knockdown by using siRNA. * P< 0.01. (D) mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines (left panel) was determined with qPCR under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Cells were incubated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α for the indicated periods under normoxic and hypoxic conditions, and then mRNA expression of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α was determined by using qPCR (right panels). * P< 0.05 compared with normoxic conditions. Values are means ± SE of triplicate samples.