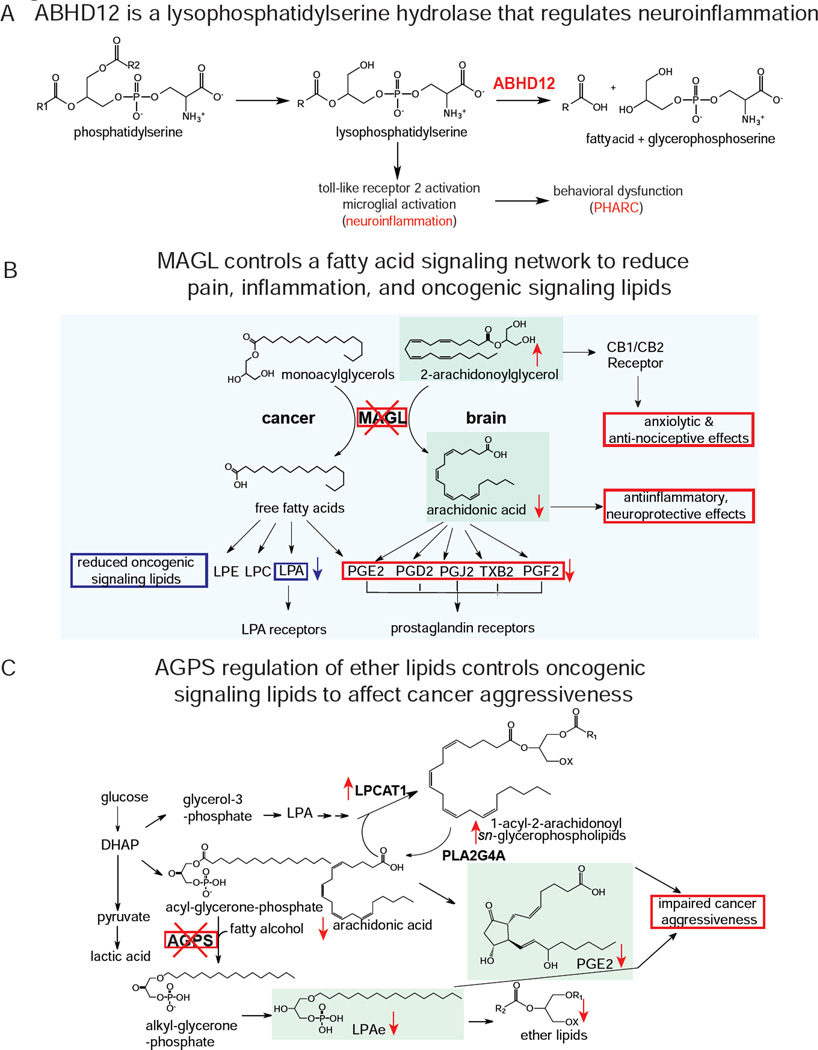
Figure 4.
Examples of metabolic pathways elucidated by metabolomic profiling. A) ABHD12 was characterized as a LPS hydrolase. ABHD12 deficiency leads to an accumulation in LPS, activates toll-like receptor 2, induces neuroinflammation, and causes a neurodegenerative disease known as PHARC. B) MAGL was shown to play critical roles of controlling endocannabinoid and eicosanoid signaling in the brain and fatty acid and fatty acid-derived oncogenic signaling lipids in cancer. MAGL blockade in brain leads to elevations in 2-AG endocannabinoid signaling and anxiolytic and anti-nociceptive effects, while also lowering the primary arachidonic acid precursor pool for pro-inflammatory eicosanoid production, leading to reduced inflammation, and neuroprotection against neurodegenerative diseases. In cancer, MAGL blockade leads to reduced fatty acids and fatty acid derived signaling lipids such as prostaglandins and lysophosphatidic acid, which impairs cancer pathogenicity. C) In cancer, AGPS was shown to not only control ether lipid synthesis, but also fatty acid metabolism that balances structural lipids with signaling lipids that fuel cancer. AGPS knockdown in cancer cells leads to reductions in the tumor-promoting lipid lysophosphatidic acid-ether, leading to a diversion of arachidonic acid away from oncogenic prostaglandins and towards structural lipids, leading to a net impairement in cancer aggressiveness.