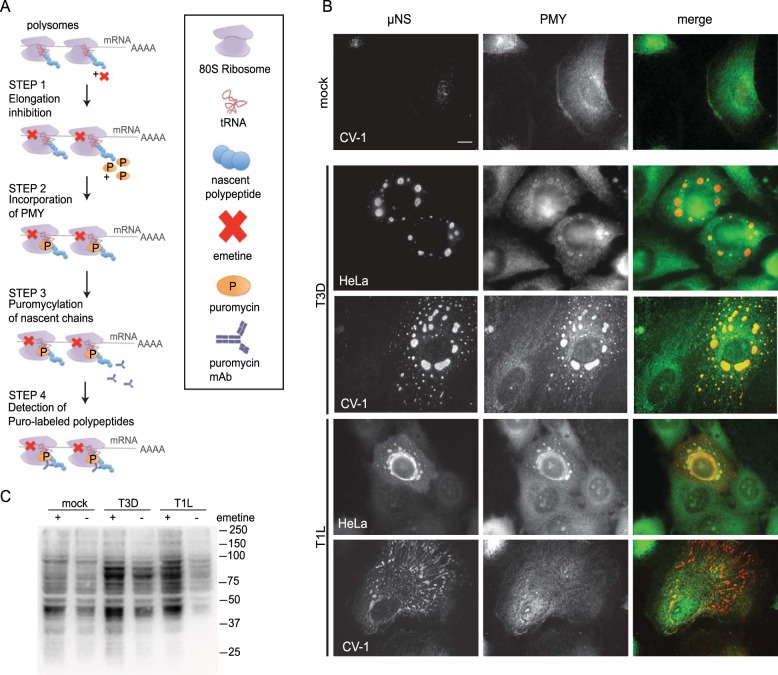
FIG 1 .
Ribopuromycylated products are synthesized in viral factories. (A) Schematic representation of the ribopuromycylation method (RPM). Addition of the inhibitor emetine “freezes” elongating ribosomes on mRNA (step 1). Puromycin (PMY) is then added (step 2) and becomes incorporated into the nascent chain (step 3). Ribosome-associated puromycylated polypeptide chains are detected with a monoclonal antibody (MAb) against PMY (step 4) and visualized by indirect immunofluorescence or immunoblotting. (B) CV-1 and HeLa cells were mock infected or infected with T3D or T1L at an MOI of 1 for 18 h before RPM processing and immunofluorescence. Representative images are shown (n ≥ 5 independent experiments). Scale bars, 10 µm. (C) CV-1 cells were infected (T1L or T3D, MOI =10) for 18 h p.i. before treatment with 208 µM emetine for 15 m at 37°C followed by RPM labeling. Puromycylated protein levels were assessed in cell lysates by immunoblotting with anti-PMY MAb.