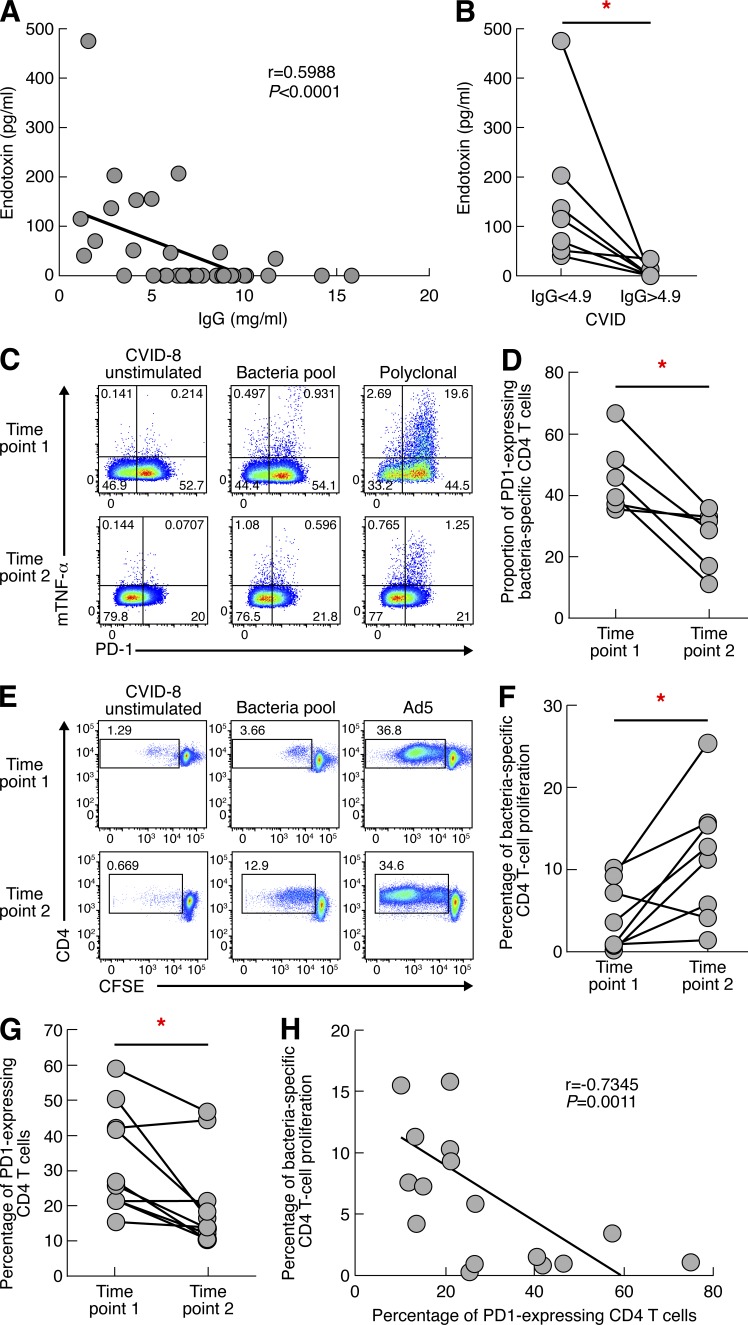
Figure 7.
Efficient IVIG treatment restores CD4 T cell functions. IgG concentration, endotoxin level, PD-1 expression, and bacteria-specific CD4 T cell proliferation were assessed on sera and blood mononuclear cells from CVID patients. (A) Correlation of endotoxin levels with IgG levels (n = 40). (B) Reduction of endotoxin levels after Ig substitution. (C) Representative flow cytometry profiles of bacteria-specific CD4 T cells expressing PD-1 in one representative CVID patient (CVID-08) at two time points. (D) Proportion of antigen-specific CD4 T cells expressing PD-1. (E) Representative flow cytometry profiles of bacteria-specific and virus-specific proliferating CD4 T cells in one representative CVID patient (CVID-8) at two time points. Unstimulated cell cultures (negative control) and cell cultures stimulated with SEB (positive control) are also shown. (F) Cumulative data of bacteria-specific CD4 T cell proliferation in treated CVID patients (n = 8). (G) Cumulative data of PD-1 expression in CD4 T cells in treated CVID patients (n = 8). (H) Correlation between bacteria-specific CD4 T cell proliferation and PD-1 expression. P-values were calculated using a paired Student’s t test for multiple comparisons in B, D, and F or Spearman Rank test for correlation in A and G. *, P < 0.05.