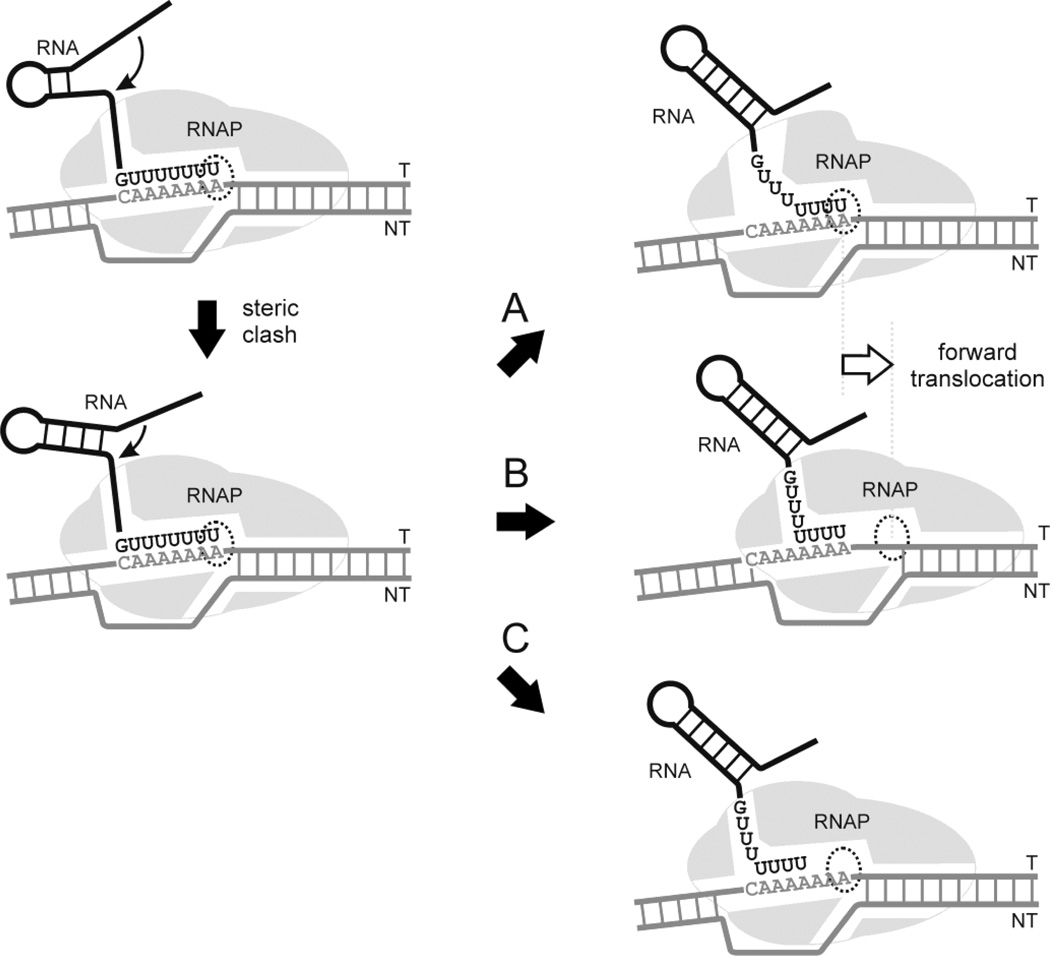
Figure 1. Models of intrinsic termination.
As the EC approaches the site of termination, complementary sequences emerge from the RNA exit pore and commence the formation of the stem-loop structure (top left panel). Continued folding of the hairpin results in steric clash with the exit pore (lower left). In the thermodynamic/allosteric model (A), steric clash disrupts interactions of the nascent transcript with the exit pore, melting of the upstream region of the RNA:DNA hybrid, and changes in protein conformation. In the forward translocation model (B) steric clash causes forward displacement of the RNAP, shortening of the hybrid due to displacement at the upstream end of the hybrid, and movement of the active site away from the 3’ end of the transcript. In the RNA pullout model (C) steric clash results in shearing of the RNA in the hybrid, altering the position of the 3’ end of the transcript in the active site.