Figure 8. Clipping planes used for streamlines with anatomical context (Skull-Hole-Model).
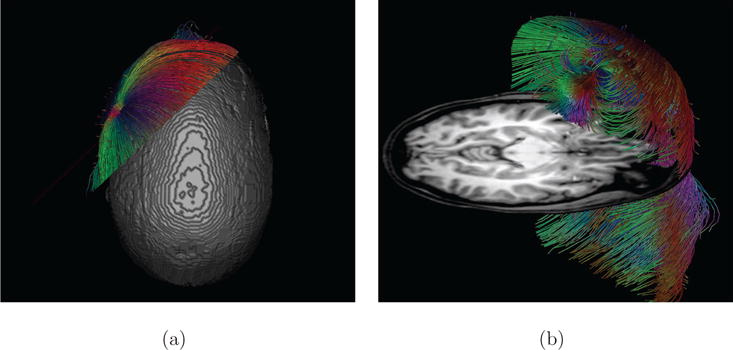
A clipping plane placed through the radially oriented source in the Skull-Hole-Model. With such a clipping plane (or a combination of planes), it is possible to select a certain fraction of the streamlines. Part (a) shows a top view of the applied clipping plane. As the isosurface prohibits the direct view onto the dipole, it is often more useful to combine interactive selection tools with orthogonal anatomy slices for orientation. In (b), such an axial slice helps to improve orientation and allows an unhindered view to the dipole. For the positions and orientations of the dipoles, see Figure 12.
