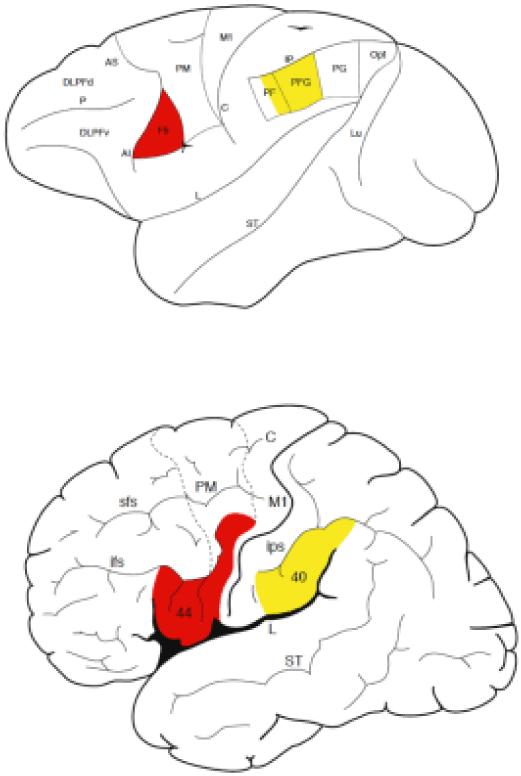
Figure 2.
Lateral view of the macaque monkey (top) and human (bottom) cerebral cortex with classical anatomical subdivision showing the areas in which mirror neurons have been found in the monkey and that in the hypothesized homolog areas of humans which: the ventral premotor cortex (red color: F5 in the monkey; lower part of the precentral gyrus, area 6, in human), part of the human inferior frontal gyrus (posterior part of area 44, and anterior part of 44 and area 45), and the inferior parietal lobule (PFG and part of PF in the monkey and area 40 in humans).